


 Equipment
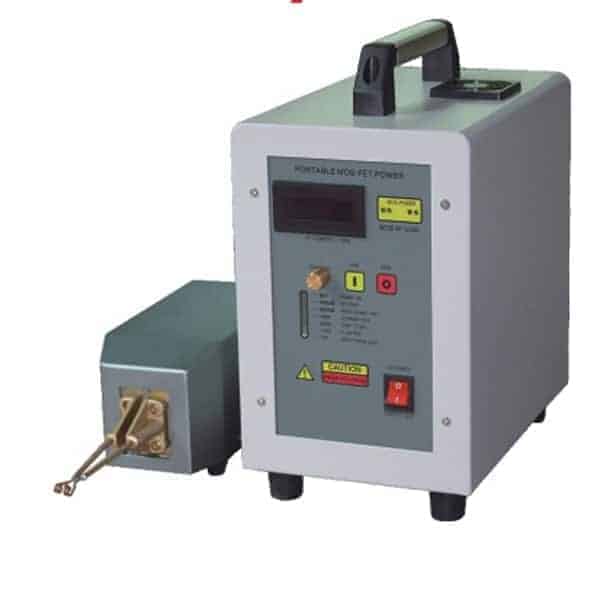
DW-UHF-6KW-III handheld induction heater
Equipment
DW-UHF-6KW-III handheld induction heater
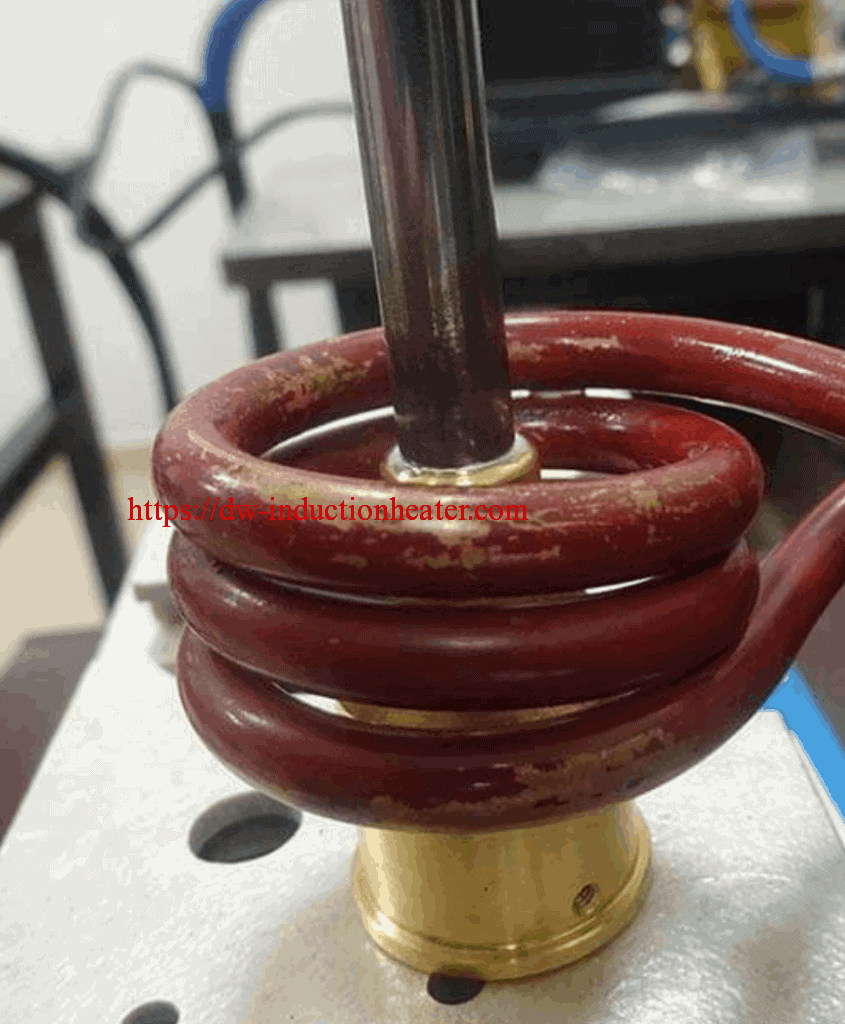
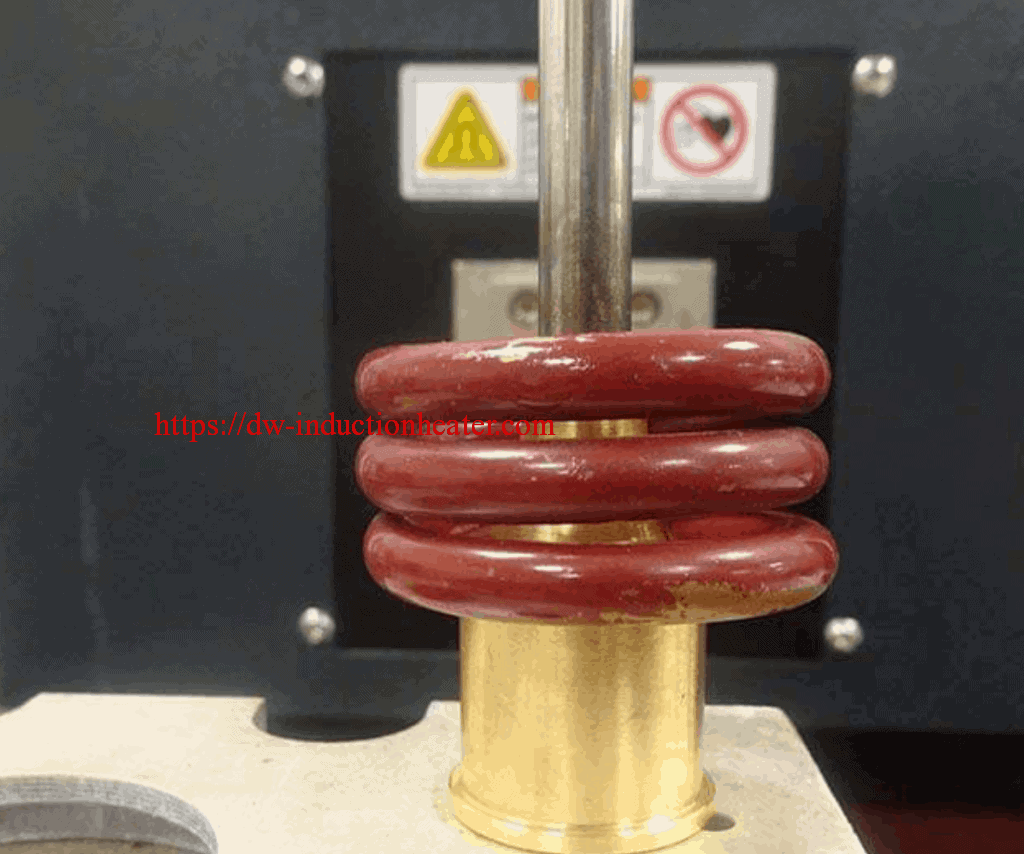




 Principles of Induction Brazing & Soldering
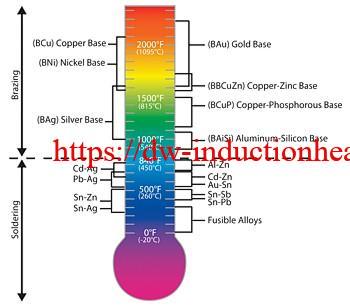
Brazing and soldering are processes of joining similar or dissimilar materials using a compatible a filler material. Filler metals include lead, tin, copper, silver, nickel and their alloys. Only the alloy melts and solidifies during these processes to join the work piece base materials. The filler metal is pulled into the joint by capillary action. Soldering processes are conducted below 840°F (450°C) while brazing applications are conducted at temperatures above 840°F (450°C) up to 2100°F (1150°C).
Principles of Induction Brazing & Soldering
Brazing and soldering are processes of joining similar or dissimilar materials using a compatible a filler material. Filler metals include lead, tin, copper, silver, nickel and their alloys. Only the alloy melts and solidifies during these processes to join the work piece base materials. The filler metal is pulled into the joint by capillary action. Soldering processes are conducted below 840°F (450°C) while brazing applications are conducted at temperatures above 840°F (450°C) up to 2100°F (1150°C).
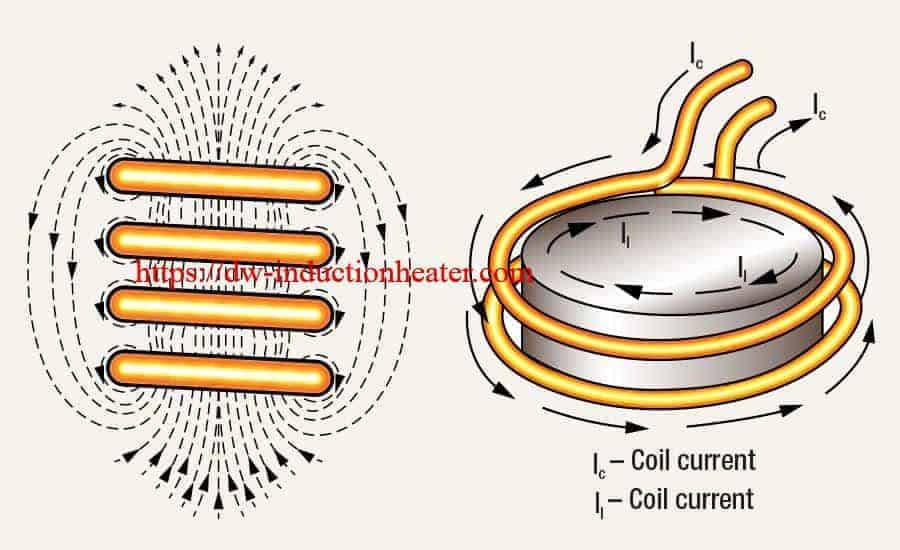
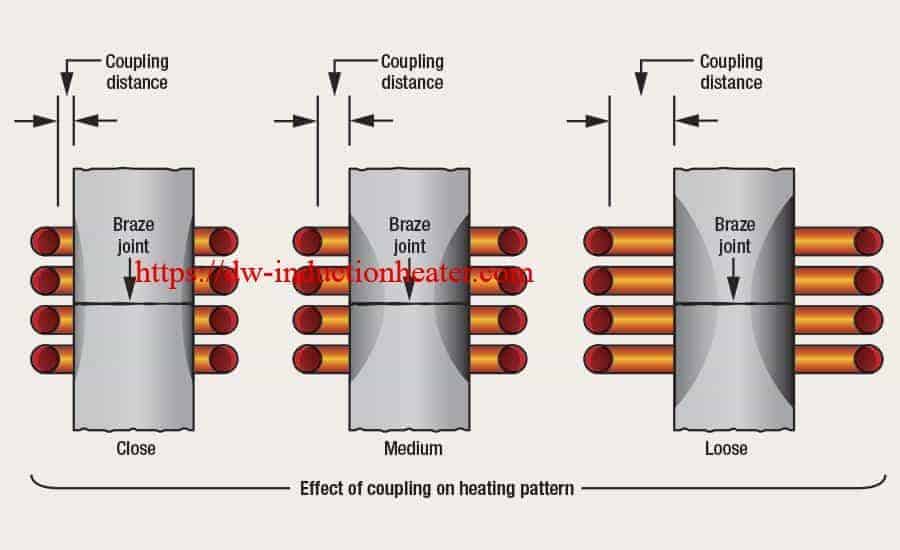 The success of these processes depends upon the assembly’s design, clearance between the surfaces to be joined, cleanliness, process control and the correct selection of equipment needed to perform a repeatable process.
The success of these processes depends upon the assembly’s design, clearance between the surfaces to be joined, cleanliness, process control and the correct selection of equipment needed to perform a repeatable process.
 Cleanliness is ordinarily obtained by introducing a flux which covers and dissolves dirt or oxides displacing them from the braze joint.
Induction Brazing Filler Materials
Induction Brazing filler metals can come in a variety of forms, shapes, sizes and alloys depending on their intended use. Ribbon, preformed rings, paste, wire and preformed washers are just a few of the shapes and forms alloys that can be found.
Cleanliness is ordinarily obtained by introducing a flux which covers and dissolves dirt or oxides displacing them from the braze joint.
Induction Brazing Filler Materials
Induction Brazing filler metals can come in a variety of forms, shapes, sizes and alloys depending on their intended use. Ribbon, preformed rings, paste, wire and preformed washers are just a few of the shapes and forms alloys that can be found.
 The decision to use a particular alloy and/or shape is largely dependent on the parent materials to be joined, placement during processing and the service environment for which the final product is intended.
Many operations are now conducted in a controlled atmosphere with a blanket of inert gas or combination of inert / active gasses to shield the operation and eliminate the need for a flux. These methods have been proven on a wide variety of material and part configurations replacing or complimenting atmosphere furnace technology with a just in time - single piece flow process.
Clearance Affects Strength
Clearance between the faying surfaces to be joined determines the amount of braze alloy, capillary action / penetration of the alloy and subsequently the strength of the finished joint. The best fit up condition for conventional silver brazing applications are 0.002 inches (0.050 mm) to 0.005 inches (0.127 mm) total clearance. Aluminum is typically 0.004 inches (0.102 mm) to 0.006 inches (0.153 mm). Larger clearances up to 0.015 inches (0.380 mm) usually lack sufficient capillary action for a successful braze.
The decision to use a particular alloy and/or shape is largely dependent on the parent materials to be joined, placement during processing and the service environment for which the final product is intended.
Many operations are now conducted in a controlled atmosphere with a blanket of inert gas or combination of inert / active gasses to shield the operation and eliminate the need for a flux. These methods have been proven on a wide variety of material and part configurations replacing or complimenting atmosphere furnace technology with a just in time - single piece flow process.
Clearance Affects Strength
Clearance between the faying surfaces to be joined determines the amount of braze alloy, capillary action / penetration of the alloy and subsequently the strength of the finished joint. The best fit up condition for conventional silver brazing applications are 0.002 inches (0.050 mm) to 0.005 inches (0.127 mm) total clearance. Aluminum is typically 0.004 inches (0.102 mm) to 0.006 inches (0.153 mm). Larger clearances up to 0.015 inches (0.380 mm) usually lack sufficient capillary action for a successful braze.
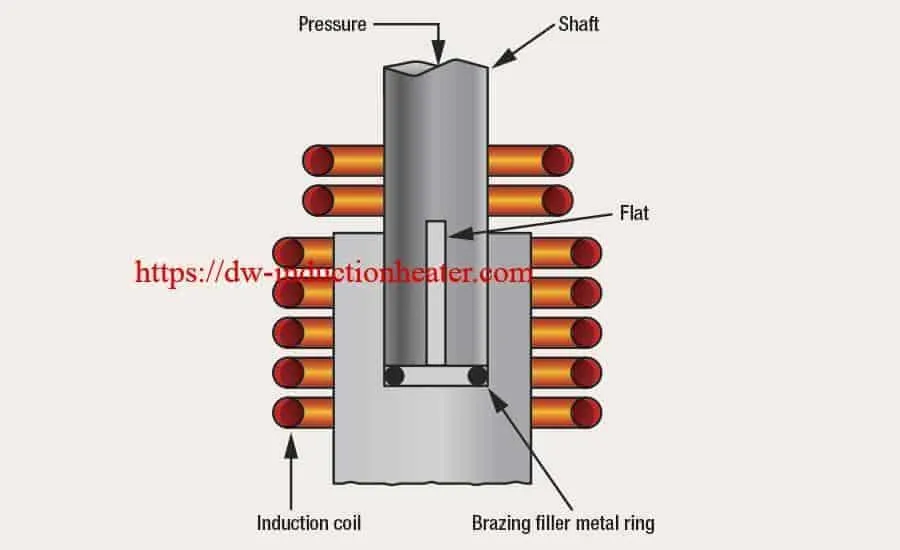
 Brazing with copper (above 1650°F / 900°C) requires the joint tolerance kept to an absolute minimum and in some cases press fit at ambient temperatures to assure minimum joint tolerances while at the brazing temperature.
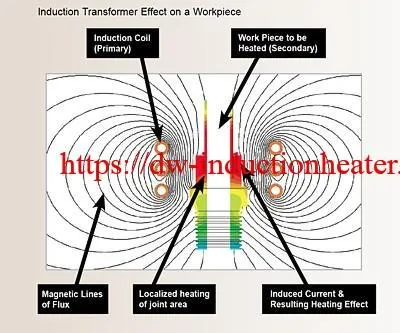
Induction heating has proven to be a valuable aid in the joining process for many reasons. Rapid heading and precise heat control offers the possibility of localized heating of high strength components without significantly changing the material properties. It also allows for the brazing of difficult materials such as aluminum and sequential, multi-alloy brazing and soldering of close proximity joints.
Brazing with copper (above 1650°F / 900°C) requires the joint tolerance kept to an absolute minimum and in some cases press fit at ambient temperatures to assure minimum joint tolerances while at the brazing temperature.
Induction heating has proven to be a valuable aid in the joining process for many reasons. Rapid heading and precise heat control offers the possibility of localized heating of high strength components without significantly changing the material properties. It also allows for the brazing of difficult materials such as aluminum and sequential, multi-alloy brazing and soldering of close proximity joints.
 Induction heating in brazing and soldering applications is readily adaptable to production line methods, permitting strategic arrangement of the equipment in an assembly line, and if necessary, heating by remote control. Frequently, induction brazing and soldering permits a reduction in the require number of part fixtures, with the minimal heating of the fixtures increasing life span and maintaining accuracy in alignment of the components to be joined. Since operators need not guide the induction heating source, both hands are left free to prepare assemblies for joining.
Induction heating in brazing and soldering applications is readily adaptable to production line methods, permitting strategic arrangement of the equipment in an assembly line, and if necessary, heating by remote control. Frequently, induction brazing and soldering permits a reduction in the require number of part fixtures, with the minimal heating of the fixtures increasing life span and maintaining accuracy in alignment of the components to be joined. Since operators need not guide the induction heating source, both hands are left free to prepare assemblies for joining.
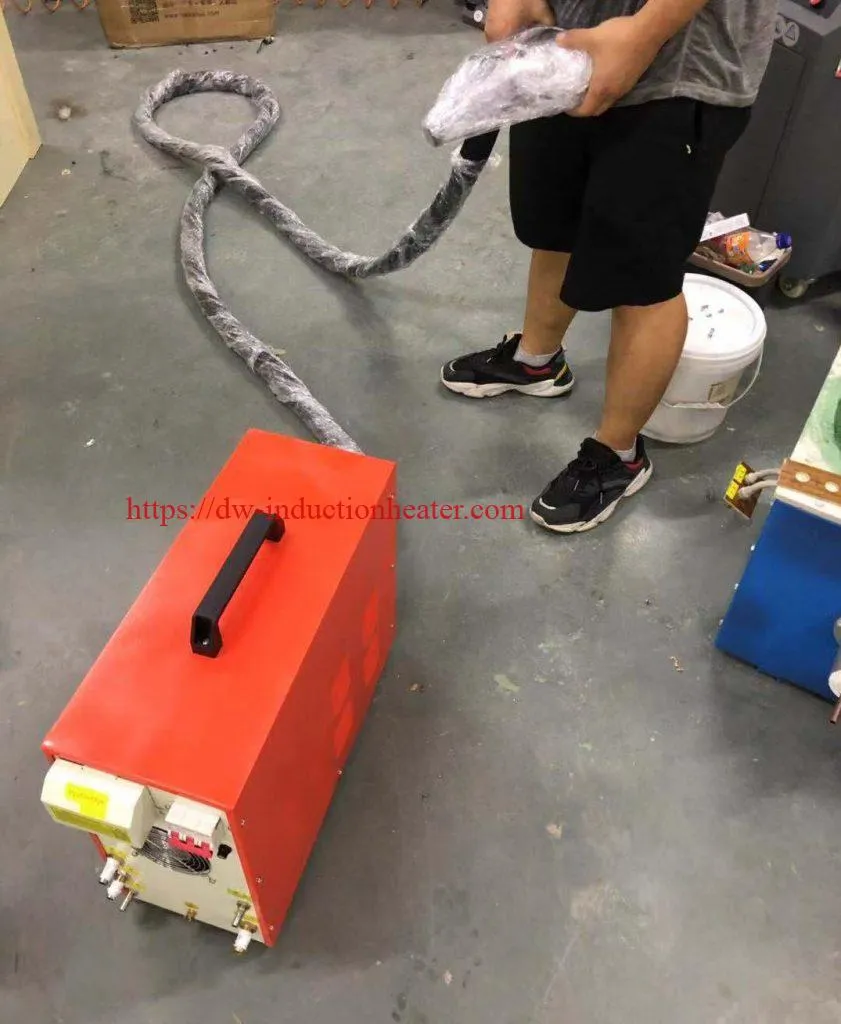 HLQ induction brazing equipment delivers quality, consistency, configurable throughput, and quick change-over tooling for various production needs. The Radyne induction brazing and soldering product line offers standard solutions for brazing:
Aluminum
Copper
Brass
Stainless steel
Carbide
And more…
HLQ induction brazing equipment delivers quality, consistency, configurable throughput, and quick change-over tooling for various production needs. The Radyne induction brazing and soldering product line offers standard solutions for brazing:
Aluminum
Copper
Brass
Stainless steel
Carbide
And more…
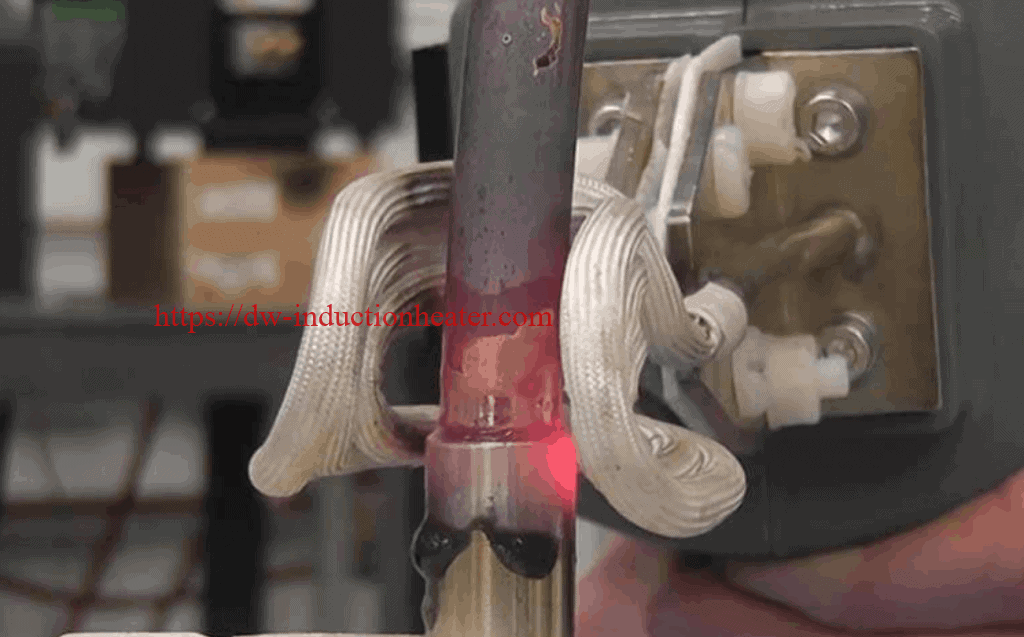
 Objective
Induction Brazing stainless steel tubing and stainless steel fittings
Equipment
DW-UHF-20kw induction brazing machine
Objective
Induction Brazing stainless steel tubing and stainless steel fittings
Equipment
DW-UHF-20kw induction brazing machine

 Results and Conclusions:
Results and Conclusions:



|
Series |
Model |
Input power Max |
Input current Max |
Oscillate frequency |
Input Voltage |
Duty cycle |
|
|
M
.
F
. |
DW-MF-15 Induction Generator |
15KW |
23A |
1K-20KHZ
According to the application |
3*380V
380V±20% |
100% |
|
|
DW-MF-25 Induction Generator |
25KW |
36A |
|||||
|
DW-MF-35Induction Generator |
35KW |
51A |
|||||
|
DW-MF-45 Induction Generator |
45KW |
68A |
|||||
|
DW-MF-70 Induction Generator |
70KW |
105A |
|||||
|
DW-MF-90 Induction Generator |
90KW |
135A |
|||||
|
DW-MF-110 Induction Generator |
110KW |
170A |
|||||
|
DW-MF-160 Induction Generator |
160KW |
240A |
|||||
|
DW-MF-45 Induction Heating Rod Forging Furnace |
45KW |
68A |
1K-20KHZ |
3*380V
380V±20% |
100% |
||
|
DW-MF-70 Induction Heating Rod Forging Furnace |
70KW |
105A |
|||||
|
DW-MF-90 Induction Heating Rod Forging Furnace |
90KW |
135A |
|||||
|
DW-MF-110 Induction Heating Rod Forging Furnace |
110KW |
170A |
|||||
|
DW-MF-160 Induction Heating Rod Forging Furnace |
160KW |
240A |
|||||
|
DW-MF-15 Induction Melting Furnace |
15KW |
23A |
1K-20KHZ |
3*380V
380V±20% |
100% |
||
|
DW-MF-25 Induction Melting Furnace |
25KW |
36A |
|||||
|
DW-MF-35 Induction Melting Furnace |
35KW |
51A |
|||||
|
DW-MF-45 Induction Melting Furnace |
45KW |
68A |
|||||
|
DW-MF-70 Induction Melting Furnace |
70KW |
105A |
|||||
|
DW-MF-90 Induction Melting Furnace |
90KW |
135A |
|||||
|
DW-MF-110 Induction Melting Furnace |
110KW |
170A |
|||||
|
DW-MF-160 Induction Melting Furnace |
160KW |
240A |
|||||
|
DW-MF-110 Induction Hardening Equipment |
110KW |
170A |
1K-8KHZ |
3*380V
380V±20% |
100% |
||
|
DW-MF-160Induction Hardening Equipment |
160KW |
240A |
|||||
|
H
.
F
. |
DW-HF-04 Series |
DW-HF-4KW-A |
4KVA |
15A |
100-250KHZ |
Single phase 220V |
80% |
|
DW-HF-15 Series |
DW-HF-15KW-A
DW-HF-15KW-B |
15KVA |
32A |
30-100KHZ |
Single phase 220V |
80% |
|
|
DW-HF-25 Series |
DW-HF-25KW-A
DW-HF-25KW-B |
25KVA |
23A |
20-80KHZ |
3*380V
380V±10% |
100% |
|
|
DW-HF-35 Series |
DW-HF-35KW-B |
35KVA |
51A |
||||
|
DW-HF-45 Series |
DW-HF-45KW-B |
45KVA |
68A |
||||
|
DW-HF-60 Series |
DW-HF-60KW-B |
60KVA |
105A |
||||
|
DW-HF-80 Series |
DW-HF-80KW-B |
80KVA |
130A |
||||
|
DW-HF-90 Series |
DW-HF-90KW-B |
90KVA |
160A |
||||
|
DW-HF-120 Series |
DW-HF-120KW-B |
120KVA |
200A |
||||
|
U
.
H
.
F
.
|
DW-UHF-3.2KW |
3.2KW |
13A |
1.1-2.0MHZ |
Single phase220V
±10% |
100% |
|
|
DW-UHF-4.5KW |
4.5KW |
20A |
|||||
|
DW-UHF-045T |
4.5KW |
20A |
|||||
|
DW-UHF-045L |
4.5KW |
20A |
|||||
|
DW-UHF-6.0KW |
6.0KW |
28A |
|||||
|
DW-UHF-06A |
6.0KW |
28A |
|||||
|
DW-UHF-6KW-B |
6.0KW |
28A |
|||||
|
DW-UHF-10KW |
10KW |
15A |
100-500KHZ |
3*380V
380V±10% |
100% |
||
|
DW-UHF-20KW |
20KW |
30A |
50-250KHZ |
||||
|
DW-UHF-30KW |
30KW |
45A |
50-200KHZ |
||||
|
DW-UHF-40KW |
40KW |
60A |
50-200KHZ |
||||
|
DW-UHF-60KW |
60KW |
90A |
50-150KHZ |
||||
 At DAWEI Induction we answer these and other key points before suggesting a brazing solution. Focus on flux Base metals must usually be coated with a solvent known as flux before they are brazed. Flux cleans the base metals, prevents new oxidation, and wets the brazing area prior to brazing. It is crucial to apply sufficient flux; too little and the flux may become
saturated with oxides and lose its ability to protect the base metals. Flux is not always needed. Phosphorous-bearing filler
can be used to braze copper alloys, brass and bronze. Flux-free brazing is also possible with active atmospheres and vacuums, but the brazing must then be performed in a controlled atmosphere chamber. Flux must normally be removed from the part once the metal filler has solidified. Different removal methods are used, the most common being water quenching, pickling and wire brushing.
At DAWEI Induction we answer these and other key points before suggesting a brazing solution. Focus on flux Base metals must usually be coated with a solvent known as flux before they are brazed. Flux cleans the base metals, prevents new oxidation, and wets the brazing area prior to brazing. It is crucial to apply sufficient flux; too little and the flux may become
saturated with oxides and lose its ability to protect the base metals. Flux is not always needed. Phosphorous-bearing filler
can be used to braze copper alloys, brass and bronze. Flux-free brazing is also possible with active atmospheres and vacuums, but the brazing must then be performed in a controlled atmosphere chamber. Flux must normally be removed from the part once the metal filler has solidified. Different removal methods are used, the most common being water quenching, pickling and wire brushing.


| DW-MF-200 | DW-MF-250 | DW-MF-300 | DW-MF-400 | DW-MF-500 | DW-MF-600 | ||
| Input Voltage | 3phases, 380V/410V/440V , 50/60Hz | ||||||
| Max Input Current | 320A | 400A | 480A | 640A | 800A | 960A | |
| Oscillating frequency | 0.5KHz^20KHz ( Oscillating frequency will be customized according to the size of heating parts) | ||||||
| Duty Cycle Loading | 100%,24h continuously work | ||||||
| Cooling Water Desires | 0.1MPa | ||||||
| Dimension | Host | 1000X800X1500mm | 1500X800X2800mm | 850X1700X1900mm | |||
| Extension | extension will be customized according to the material and size of heating parts | ||||||
| Weight | 110kg | 150kg | 160kg | 170kg | 200kg | 220kg | |
| Depend on the dimension of extension | |||||||
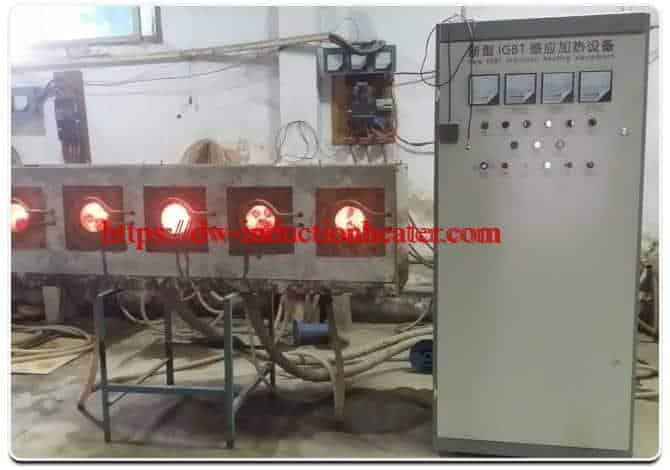
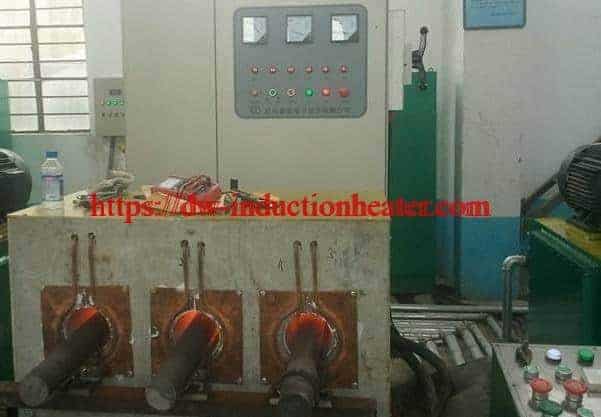


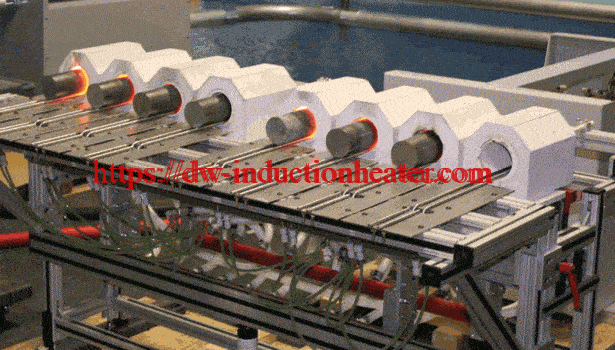

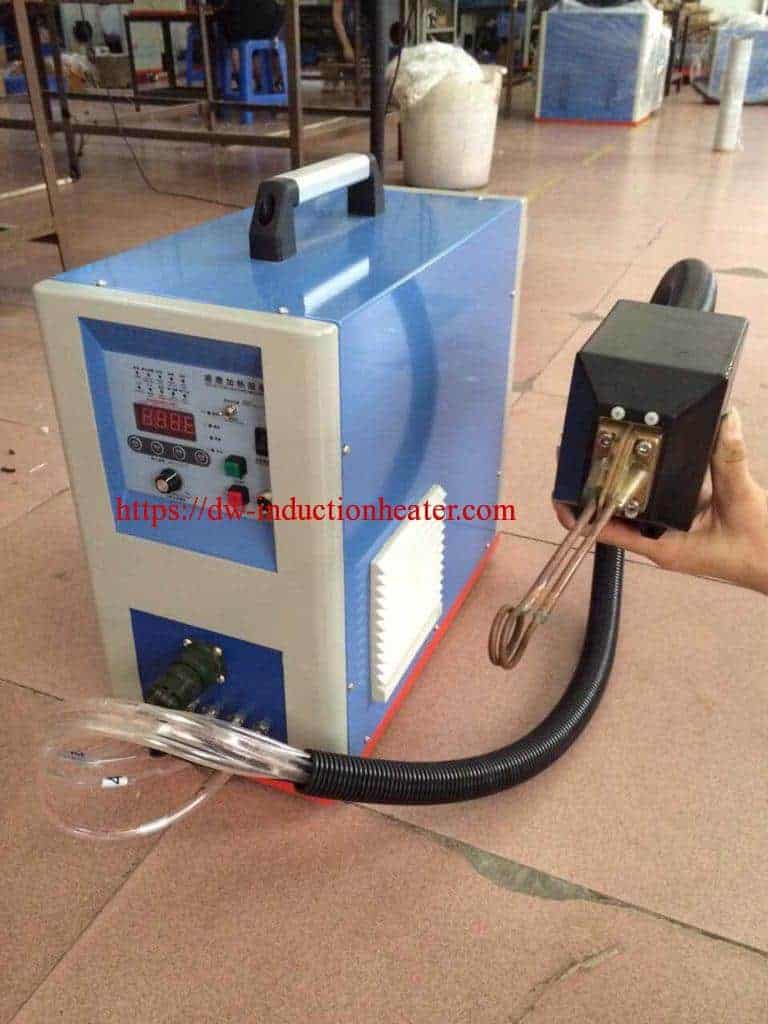
 Equipment:
HLQ DW-UHF-6kW-III air-cooled induction heating system was utilized in the annealing process. Tempilaq paint was used to determine if the desired temperature in the annealed area is reached.
Equipment:
HLQ DW-UHF-6kW-III air-cooled induction heating system was utilized in the annealing process. Tempilaq paint was used to determine if the desired temperature in the annealed area is reached.


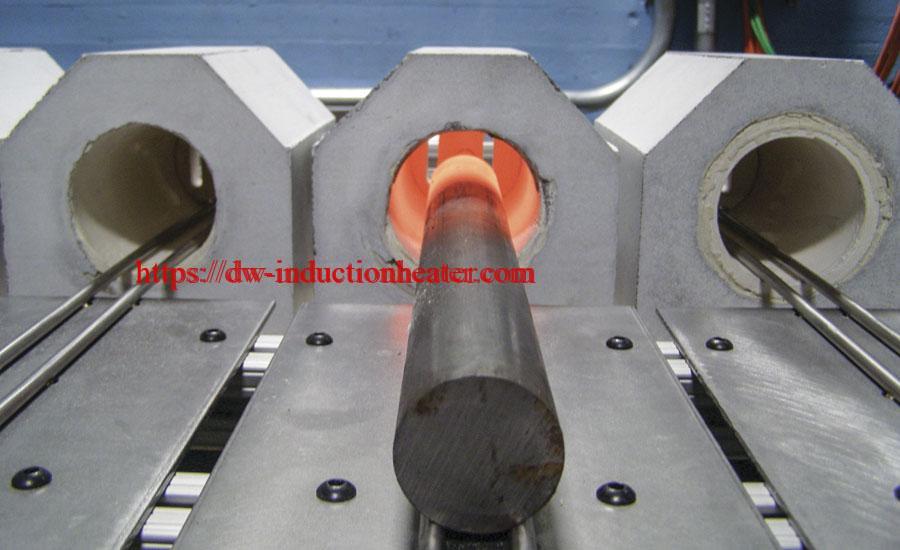
 Induction heating provides improved control of the annealing process. Repeatable heating profiles can easily be obtained by precise regulation of the heating power. Since the workpiece is directly heated by the magnetic field, a faster response can be achieved. Moreover, the high overall efficiency of the induction heating process is crucial for such lengthy treatment.
Compared to most of the standard methods, induction annealing is a clean and easy to automate, contactless approach providing a high quality of the treated workpieces.
Induction heating provides improved control of the annealing process. Repeatable heating profiles can easily be obtained by precise regulation of the heating power. Since the workpiece is directly heated by the magnetic field, a faster response can be achieved. Moreover, the high overall efficiency of the induction heating process is crucial for such lengthy treatment.
Compared to most of the standard methods, induction annealing is a clean and easy to automate, contactless approach providing a high quality of the treated workpieces.
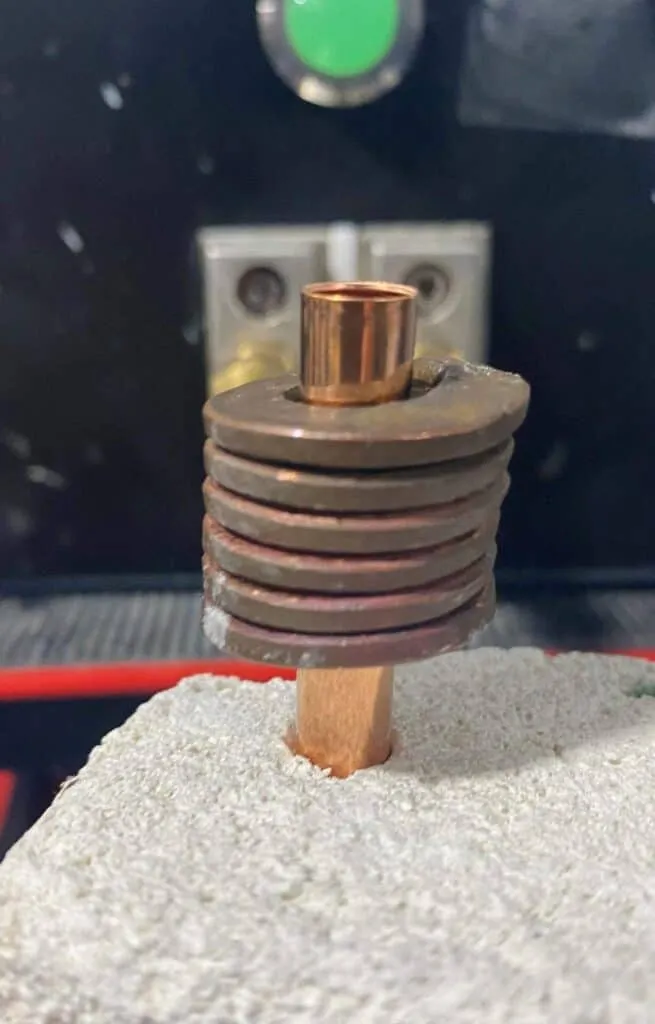
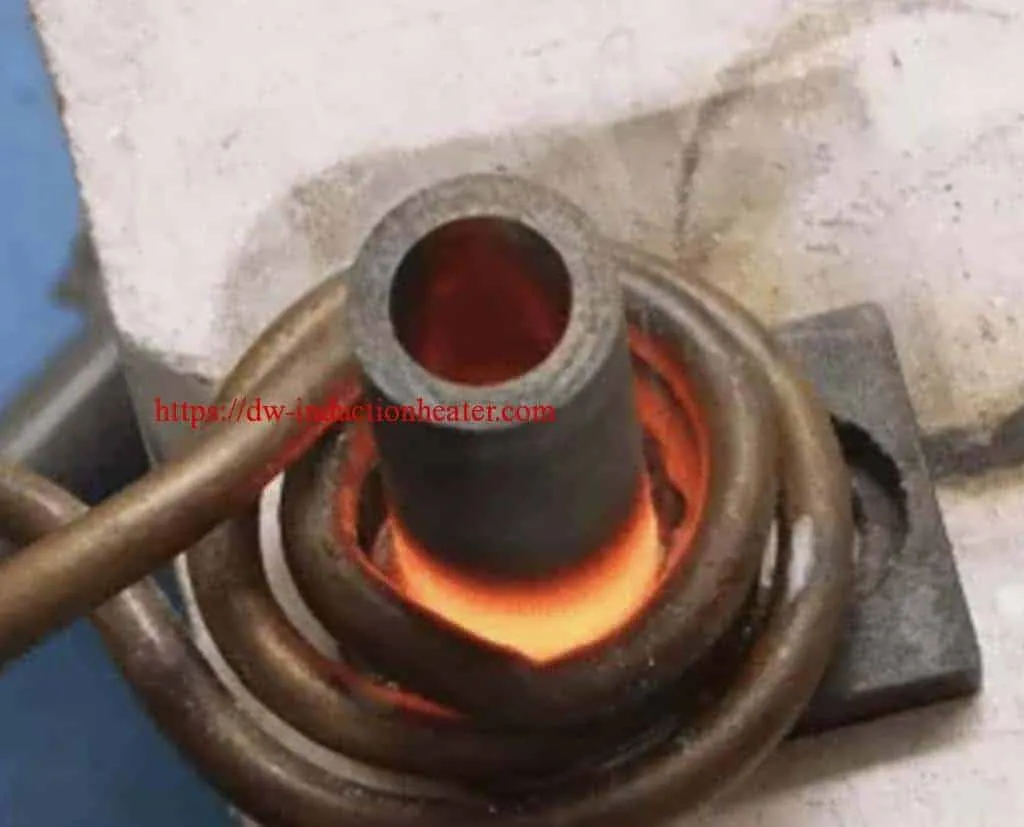
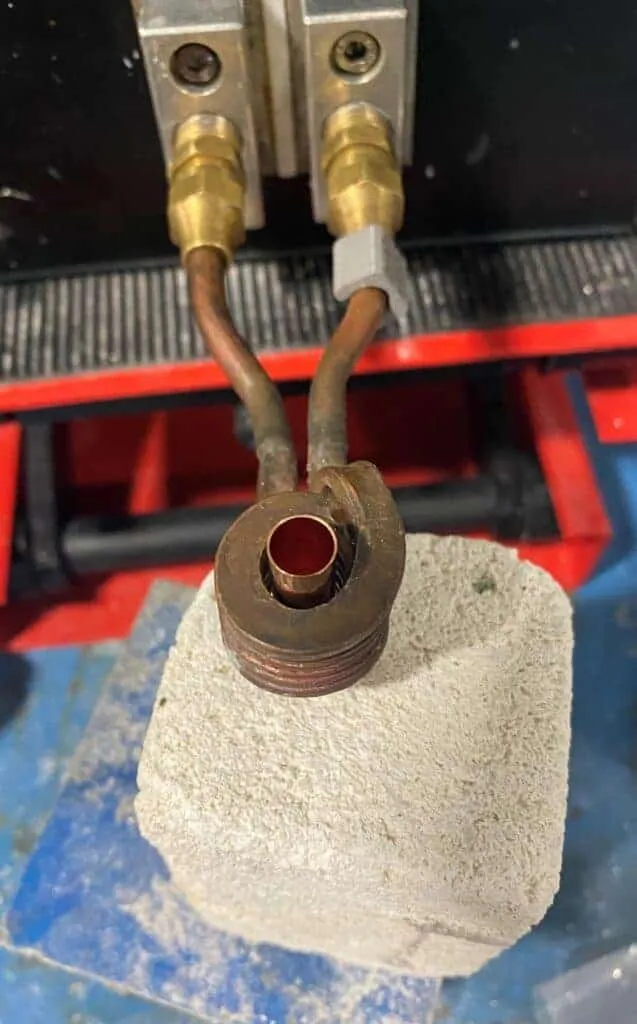
 Objective
Brazing carbide onto steel workpiece
Equipment
DW-UHF-6KW-III Handheld Induction Brazing Heater
Objective
Brazing carbide onto steel workpiece
Equipment
DW-UHF-6KW-III Handheld Induction Brazing Heater
 Key Parameters
Power: 4kW
Temperature: Approximately 1500°F (815°C)
Time: 16 sec
Materials
Coil-
2 helical turns (20 mm ID)
1 planar turn (40 mm OD, 13 mm Height)
Carbide-
13 mm OD, 3 mm wall thickness
Steel piece–
20 mm OD, 13 mm ID
Key Parameters
Power: 4kW
Temperature: Approximately 1500°F (815°C)
Time: 16 sec
Materials
Coil-
2 helical turns (20 mm ID)
1 planar turn (40 mm OD, 13 mm Height)
Carbide-
13 mm OD, 3 mm wall thickness
Steel piece–
20 mm OD, 13 mm ID
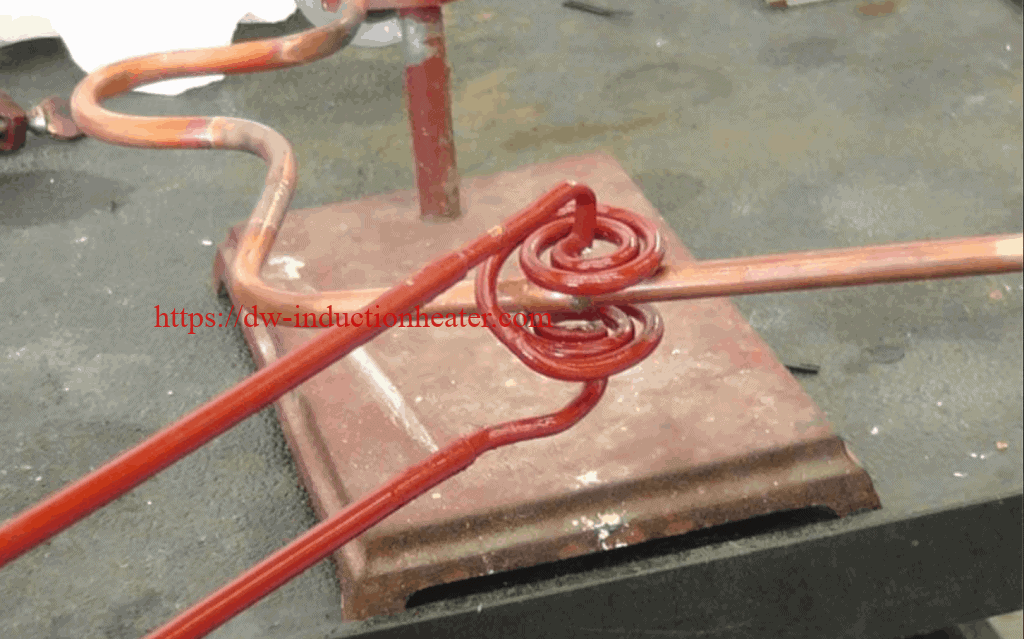
 Materials
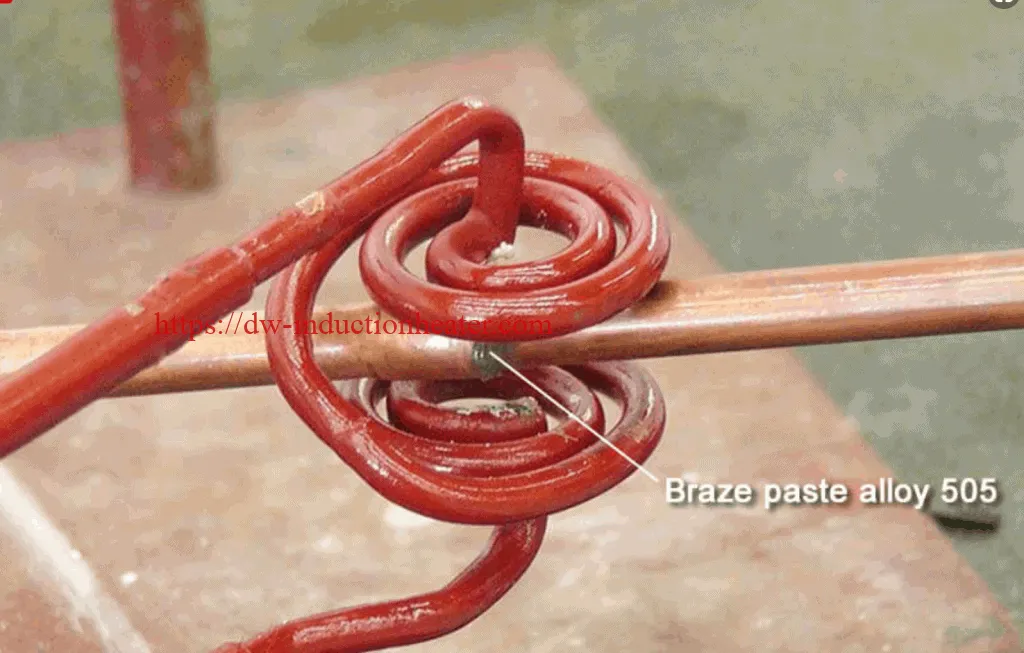
• Copper tubing – Suction Tube
• Braze paste
Key Parameters
Power: 9.58 kW
Temperature: Approximately 1500° F (815° C)
Time: 5 – 5.2 sec
Materials
• Copper tubing – Suction Tube
• Braze paste
Key Parameters
Power: 9.58 kW
Temperature: Approximately 1500° F (815° C)
Time: 5 – 5.2 sec
 Results/Benefits:
Results/Benefits:
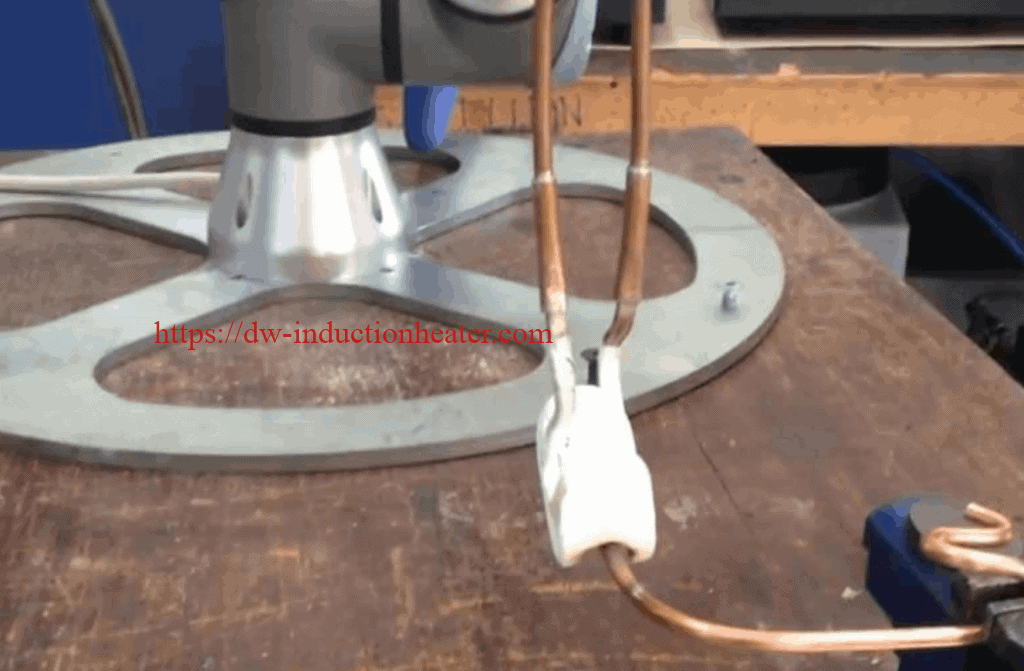


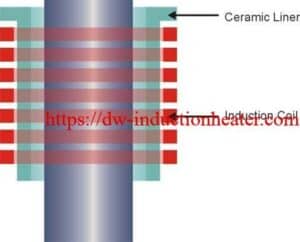
 HLQ team was provided with 2 different parts to be brazed in our test laboratory.
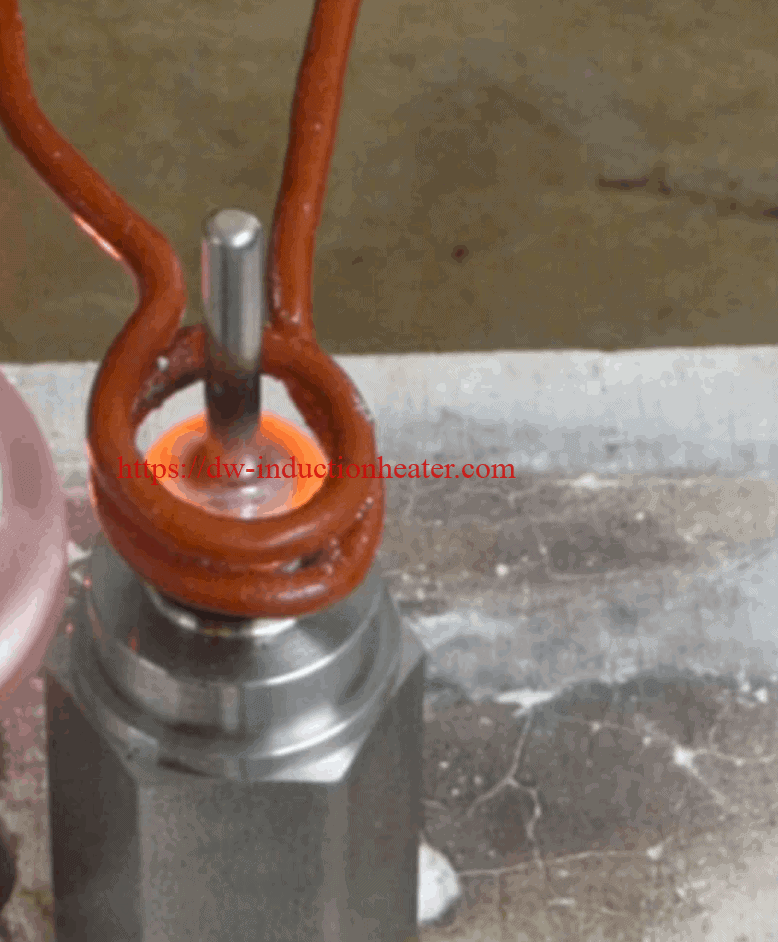
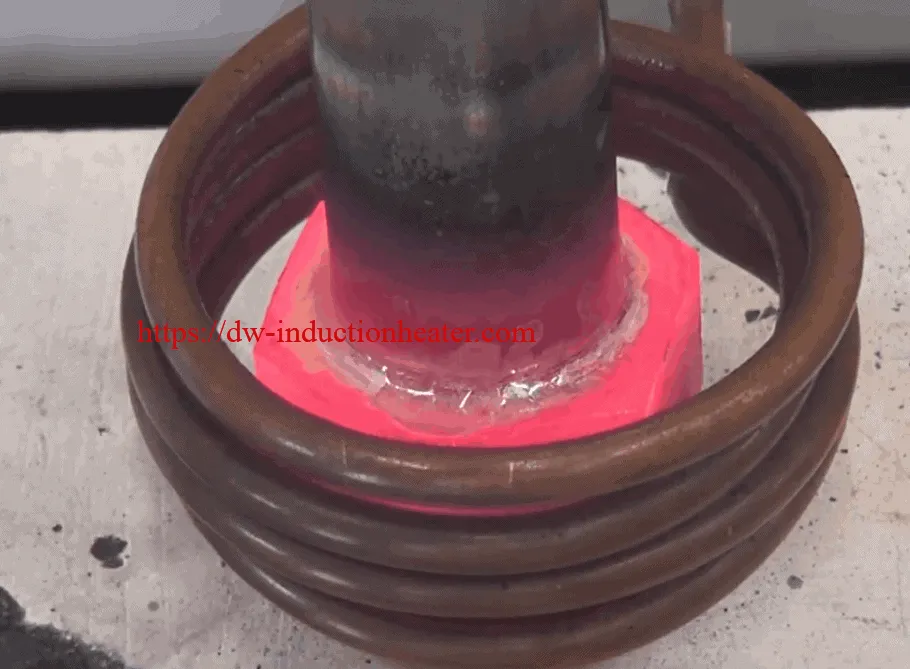
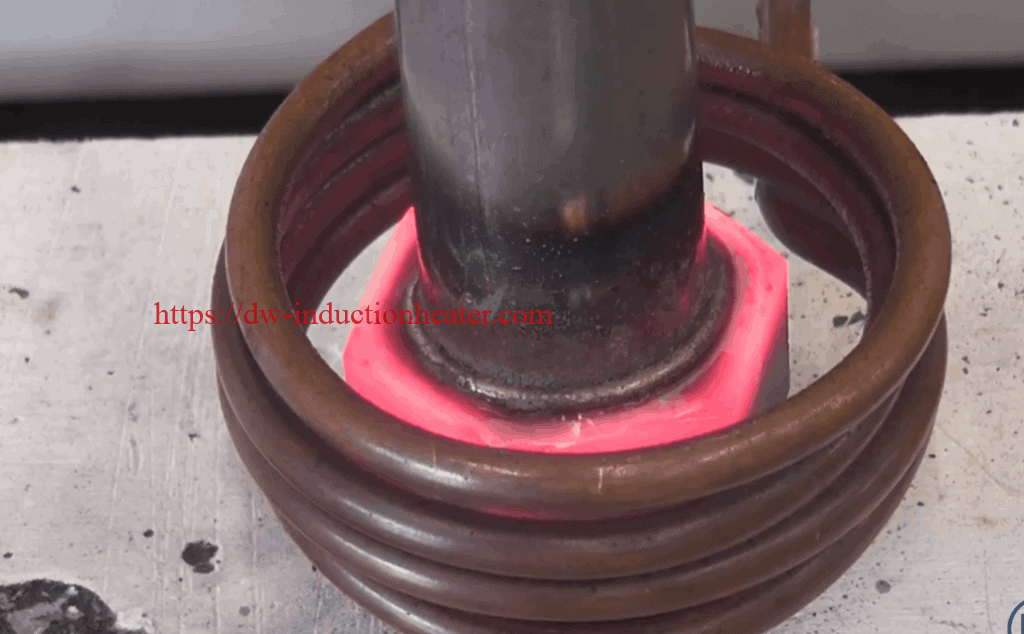
Objective: Induction Brazing of a 0.15’’/ 3.81mm stainless steel pin to a steel base.
Equipment: DW-UHF-6KW-III handheld induction brazing system
Industry: Appliances & HVAC
HLQ team was provided with 2 different parts to be brazed in our test laboratory.
Objective: Induction Brazing of a 0.15’’/ 3.81mm stainless steel pin to a steel base.
Equipment: DW-UHF-6KW-III handheld induction brazing system
Industry: Appliances & HVAC
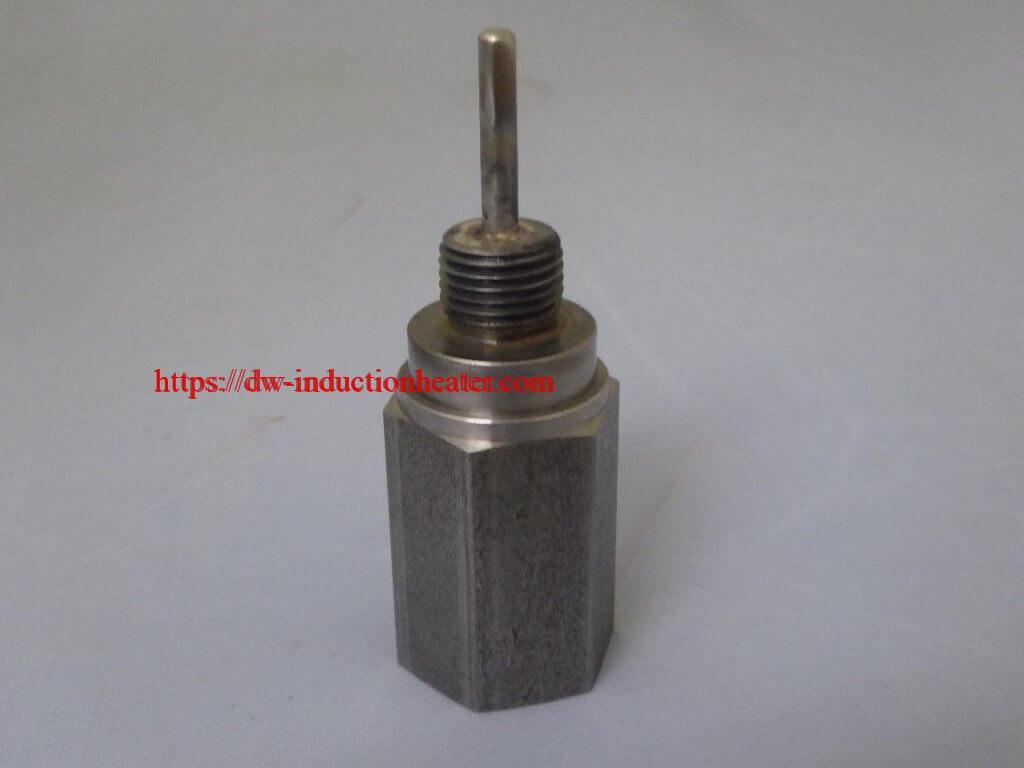
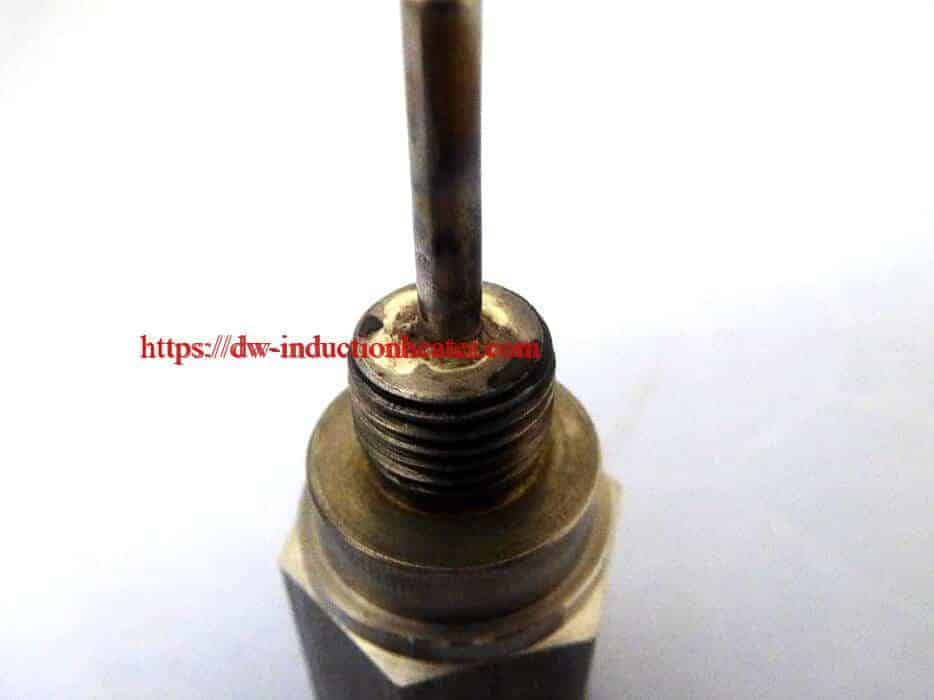 Materials:
Steel hexagon (base 1’’/ 25.4 mm diameter; 0.1’’/ 2.54 mm wall thickness)
A stainless steel pin (0.15’’/ 3.81 mm)
Materials:
Steel hexagon (base 1’’/ 25.4 mm diameter; 0.1’’/ 2.54 mm wall thickness)
A stainless steel pin (0.15’’/ 3.81 mm) Other Materials:
All-purpose black brazing flux
Power: 1.43 kW
Temperature: 1400 °F/ 760°C
Time: 8 seconds
Process:
The two workpieces were carefully positioned together. All-purpose induction brazing black flux was added because it is ideal for high-temperature applications where rapid, localized heating is needed. The process of induction brazing was performed successfully within 8 seconds by using the DW-UHF-6KW-III handheld induction brazing system, producing the induction heating power of 1.43 kW at 1400 °F/ 760°C.
Other Materials:
All-purpose black brazing flux
Power: 1.43 kW
Temperature: 1400 °F/ 760°C
Time: 8 seconds
Process:
The two workpieces were carefully positioned together. All-purpose induction brazing black flux was added because it is ideal for high-temperature applications where rapid, localized heating is needed. The process of induction brazing was performed successfully within 8 seconds by using the DW-UHF-6KW-III handheld induction brazing system, producing the induction heating power of 1.43 kW at 1400 °F/ 760°C.

