Induction heating coil design involves creating a coil that can generate an alternating magnetic field with enough power to heat a metal object.
Induction heating is a widely-used process that involves heating metal objects without direct contact. This technique has revolutionized industries ranging from automotive to aerospace and is now widely adopted in manufacturing and research settings. One of the most critical components of an induction heating system is the induction coil. The design of the coil plays a crucial role in the efficiency, accuracy, and performance of the system. For engineers working in the field of induction heating, understanding the principles of coil design is essential. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide to induction heating coil design, covering the basic principles, types of coils, and factors to consider during the design process. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced professional, this guide will provide you with the knowledge and tools you need to design and optimize induction heating coils for your specific application.
1. Introduction to induction heating and induction coil design
Induction heating is a process that uses an electromagnetic field to heat up a material. It is a popular method used in various industries, such as metalworking, automotive, and aerospace. One of the critical components of induction heating is the induction coil. The induction coil is responsible for creating the electromagnetic field that heats up the material. The design of the induction coil is a crucial factor in the induction heating process. In this guide, we will introduce you to induction heating and induction coil design to help you design a successful induction heating system. We will start by discussing the basics of induction heating, including how it works, its advantages, and its applications. We will then dive into induction coil design, covering the key factors that influence the design process, including coil shape, size, and materials. We will also discuss different types of induction coils, such as air-core and ferrite-core coils, and their respective advantages and disadvantages. By the end of this guide, you will have a solid understanding of induction heating and induction coil design, and you will be able to design your own induction heating system.
2. Basic principles of induction coil design
The basic principles of
induction coil design are straightforward. The purpose of an induction coil is to transfer electrical power from the power source to the workpiece. This is accomplished by creating a magnetic field that
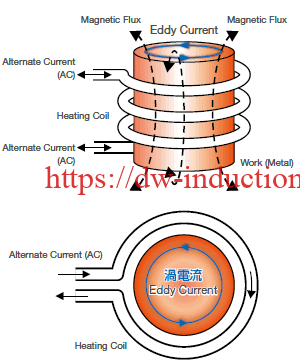
surrounds the workpiece. When the workpiece is placed in the magnetic field, electrical current is induced in the workpiece. The amount of electrical current that is induced in the workpiece is directly proportional to the strength of the magnetic field that surrounds it. The first step in designing an induction coil is to determine the size and shape of the workpiece that will be heated. This information will be critical in determining the size and shape of the coil that will be needed. Once the size and shape of the workpiece have been determined, the next step is to calculate the amount of power that will be needed to heat the workpiece to the desired temperature. The basic principles of induction coil design also include the selection of the appropriate materials for the coil. The coil needs to be made of materials that can withstand the high temperatures and magnetic fields that are generated during the heating process. The type of material that is used for the coil will depend on the specific application and the temperature requirements. Overall, understanding the basic principles of induction coil design is essential for engineers who are designing induction heating systems. With this knowledge, they will be able to create efficient and effective heating systems that meet the specific needs of their applications.
3. Types of induction coils
There are several types of induction coils that engineers can use in their designs, depending on the application and requirements. Here are some of the most common types:
1. Pancake Coil: This type of coil is flat and circular, with the turns of the coil parallel to the ground. It is commonly used for heating flat objects, such as sheets of metal or plastic.
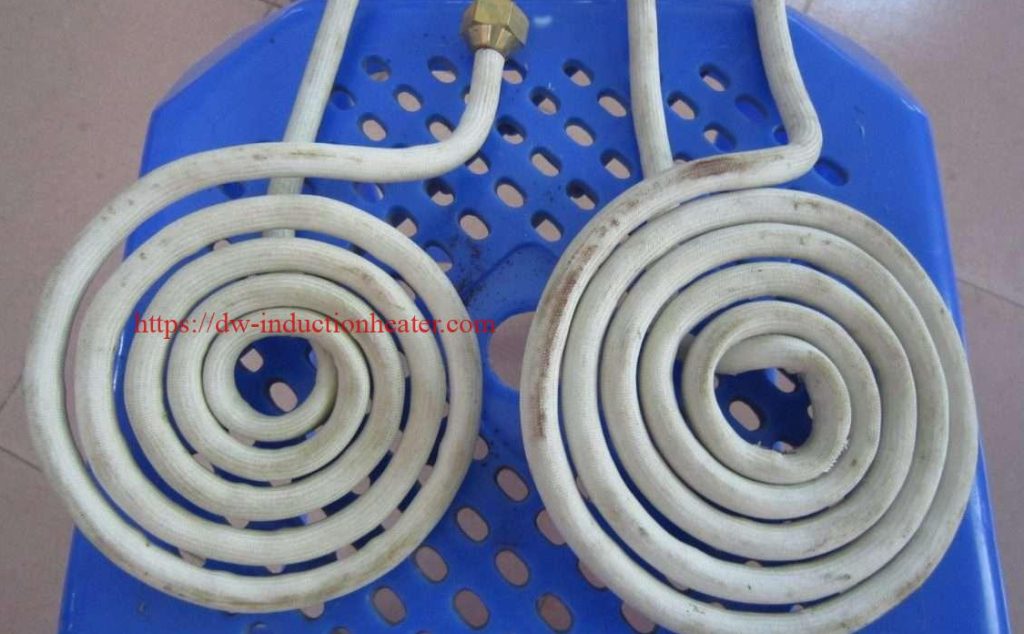

2. Helical Coil: This coil has a cylindrical shape, with the turns of the coil going around the length of the cylinder. It is commonly used for heating long, thin objects such as wires, rods or tubes.
3. Cylindrical Coil: This coil has a cylindrical shape, but the turns of the coil go around the circumference of the cylinder. It is commonly used for heating large, cylindrical objects such as pipes or tubes.

4. Concentric Coil: This type of coil consists of two or more coils, with the turns of each coil placed concentrically around each other. It is commonly used for heating smaller objects, or for applications where precise control over the heating pattern is required.
5. Custom Coils: Engineers may also design custom coils for specific applications, such as irregularly shaped objects or unique heating requirements.
These coils can be very complex and require advanced design techniques. By understanding the different types of induction coils available, engineers can select the right coil for their application and optimize the performance of their induction heating systems.
4.Factors Involved in Induction Heating Coil Design:
1. Coil Geometry:
The geometry of the coil is an important factor in determining the effectiveness of the induction heating process. There are different shapes of coils, including circular, square, and rectangular. The shape and dimensions of the coil will determine the distribution of energy within the heated object. The geometry of the coil should be such that the energy is distributed evenly, and there are no cold spots.
2. Coil Material:
The material used to make the coil also plays a significant role in the efficiency of the induction heating process. The choice of material depends on the frequency of the alternating magnetic field used and the temperature of the heated object. Generally, copper and aluminum are the commonly used materials for induction heating coils. Copper is the most preferred material because of its high conductivity and resistance to high temperatures.
3. Number of Turns:
The number of turns in the
induction heating coil also affects the efficiency of the process. The number of turns determines the distribution of the voltage and current within the coil, which directly affects the energy transfer to the heated object. Generally, a higher number of turns in the coil will increase the resistance, which will result in lower efficiency.
4. Cooling Mechanism:
The cooling mechanism used in the induction heating coil also plays a critical role in the design. The cooling mechanism ensures that the coil does not overheat during operation. There are different types of cooling mechanisms, including air cooling, water cooling, and liquid cooling. The choice of cooling mechanism depends on the temperature of the heated object, the frequency of the alternating magnetic field, and the power rating of the coil.
Conclusion:
The
induction heating coil design is critical to the efficiency and effectiveness of the induction heating process. The geometry, material, number of turns, and cooling mechanism are the key factors involved in the design. To achieve optimal performance, the coil should be designed such that the energy is distributed evenly within the heated object. Additionally, the material used to make the coil should have high conductivity and resistance to high temperatures. Finally, the cooling mechanism used in the coil should be selected based on the temperature of the heated object, the frequency of the alternating magnetic field and the power rating of the coil.
 2. Helical Coil: This coil has a cylindrical shape, with the turns of the coil going around the length of the cylinder. It is commonly used for heating long, thin objects such as wires, rods or tubes.
3. Cylindrical Coil: This coil has a cylindrical shape, but the turns of the coil go around the circumference of the cylinder. It is commonly used for heating large, cylindrical objects such as pipes or tubes.
2. Helical Coil: This coil has a cylindrical shape, with the turns of the coil going around the length of the cylinder. It is commonly used for heating long, thin objects such as wires, rods or tubes.
3. Cylindrical Coil: This coil has a cylindrical shape, but the turns of the coil go around the circumference of the cylinder. It is commonly used for heating large, cylindrical objects such as pipes or tubes.
 4. Concentric Coil: This type of coil consists of two or more coils, with the turns of each coil placed concentrically around each other. It is commonly used for heating smaller objects, or for applications where precise control over the heating pattern is required.
5. Custom Coils: Engineers may also design custom coils for specific applications, such as irregularly shaped objects or unique heating requirements.
These coils can be very complex and require advanced design techniques. By understanding the different types of induction coils available, engineers can select the right coil for their application and optimize the performance of their induction heating systems.
4. Concentric Coil: This type of coil consists of two or more coils, with the turns of each coil placed concentrically around each other. It is commonly used for heating smaller objects, or for applications where precise control over the heating pattern is required.
5. Custom Coils: Engineers may also design custom coils for specific applications, such as irregularly shaped objects or unique heating requirements.
These coils can be very complex and require advanced design techniques. By understanding the different types of induction coils available, engineers can select the right coil for their application and optimize the performance of their induction heating systems.

