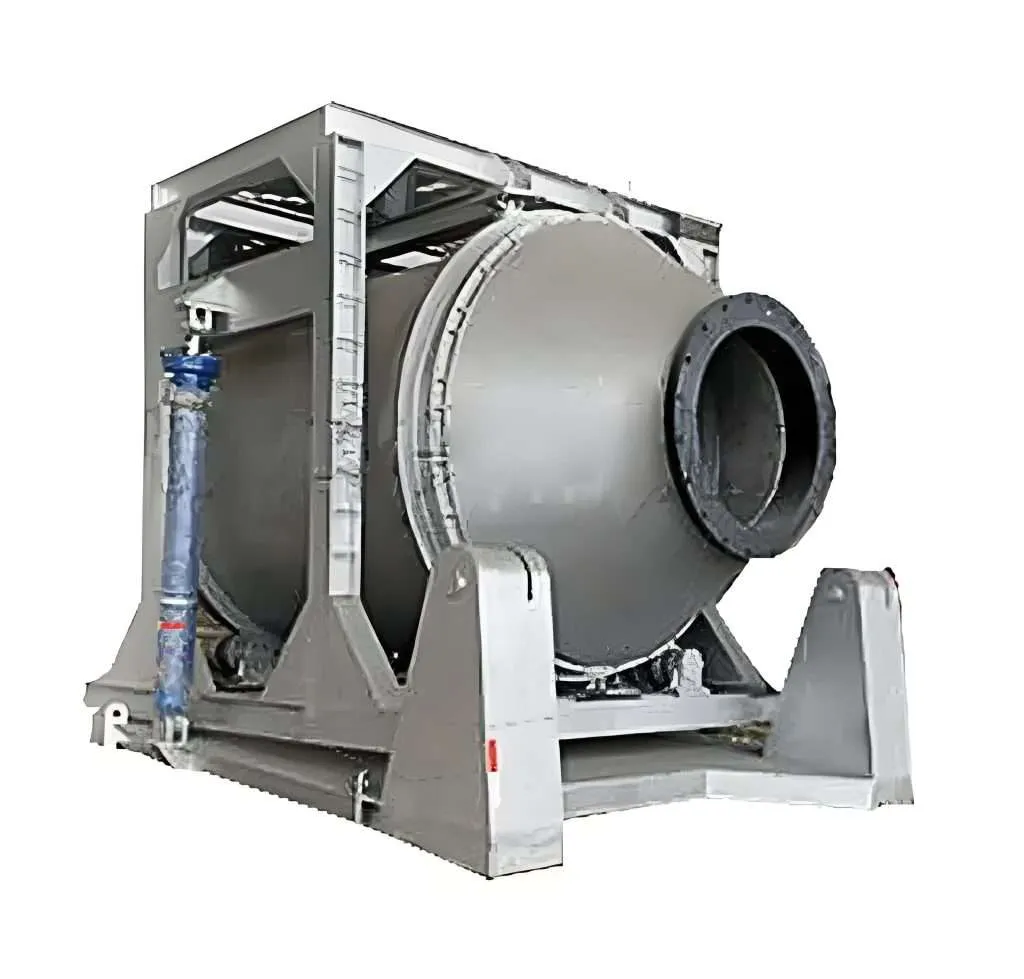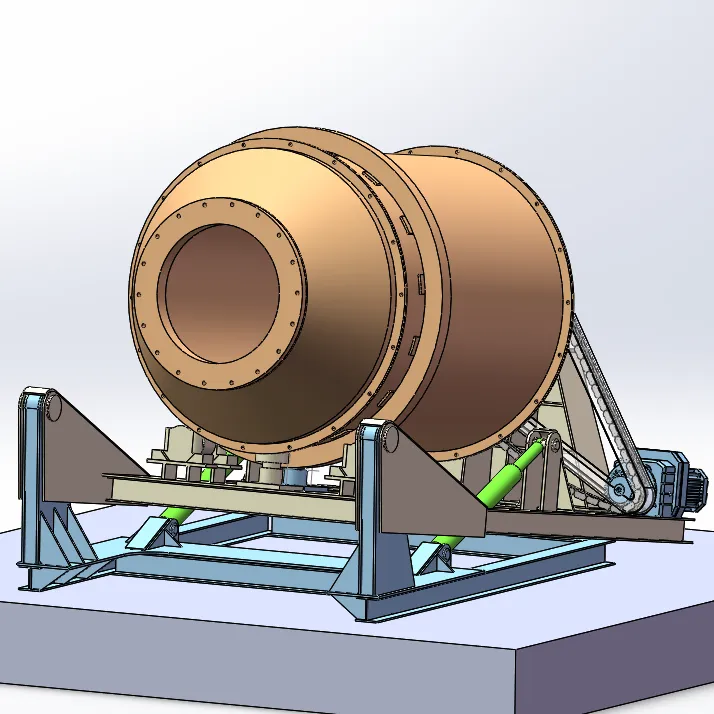
A tilting rotary furnace is a type of industrial furnace designed for the efficient melting, refining, and processing of metals. This specialized furnace combines the functionalities of a rotary furnace with the added flexibility of a tilting mechanism. Here’s a detailed look at what a tilting rotary furnace is and its key features:
 In summary, a tilting rotary furnace is a versatile and efficient industrial furnace that plays a critical role in modern metallurgy, particularly in metal recycling, foundries, and production of high-quality metal products. Its design facilitates superior metal handling, energy efficiency, and precise control, which are highly valued in metalworking industries.
In summary, a tilting rotary furnace is a versatile and efficient industrial furnace that plays a critical role in modern metallurgy, particularly in metal recycling, foundries, and production of high-quality metal products. Its design facilitates superior metal handling, energy efficiency, and precise control, which are highly valued in metalworking industries.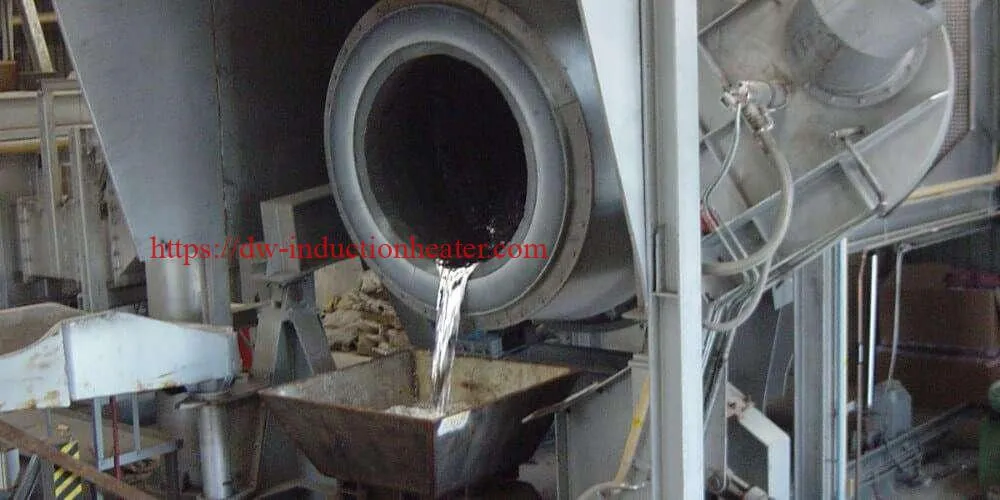
 Key Features of a Tilting Rotary Furnace
Key Features of a Tilting Rotary Furnace
- Rotary Mechanism:
- Rotary Drum: The furnace typically consists of a cylindrical, rotating drum where the metal charge is placed. The rotation helps to evenly distribute heat and mix the molten metal, which promotes uniform melting and alloying.
- Efficient Heating: The rotary action ensures that the entire metal charge is exposed to the heat source, which improves melting efficiency and reduces melting times.
- Tilting Mechanism:
- Tilted Pouring: The furnace can be tilted to pour the molten metal out of the drum smoothly and accurately into pouring molds, ladles, or casting machines. This mechanization reduces manual labor and increases safety.
- Precision Control: The tilt control is usually precise, allowing operators to manage the flow of molten metal carefully, which is essential for high-quality casting operations.

- Heating System:
- Fuel Options: Tilting rotary furnaces can be designed to use different types of fuel, including natural gas, diesel, propane, or electricity for heating. The choice of fuel can depend on economic and environmental considerations.
- Burners and Airflow: The heating system includes burners and air passages designed for efficient combustion and heat transfer. Some advanced models have regenerative burners to recover waste heat and improve energy efficiency.
- Material Handling:
- Scrap Loading: These furnaces are suitable for melting a variety of scrap types, from loose and fragmented pieces to compact bales and ingots.
- Residue Handling: The rotary movement also helps in managing residues like dross and slag, which can be removed more easily compared to traditional static furnaces.
- Advanced Controls:
- Temperature Control: Precise temperature controls and monitoring systems ensure that the metal is melted to the desired specifications, which is crucial for producing high-quality alloys and castings.
- Automation: Many modern tilting rotary furnaces are equipped with automated control systems that enhance operational efficiency and safety.

Applications of Tilting Rotary Furnaces
- Metal Recycling:
- Used extensively for recycling aluminum, zinc, lead, and other non-ferrous metals. The efficient melting process helps recover high-purity metal from scrap.
- Foundries and Casting Operations:
- Utilized for melting primary metals and alloys in foundry operations. The ease of pouring and precise control make it suitable for producing quality castings.
- Die Casting:
- Provides a consistent supply of molten metal for die casting processes. This is particularly important in industries like automotive manufacturing, where precision and quality are crucial.
- Extrusion Plants:
- Prepares billets for the extrusion process. The uniform heating of the billets ensures optimal extrusion performance.
- Aerospace Industry:
- Produces high-quality alloys needed for critical aerospace components, ensuring they meet strict industry standards.
- Continuous Casting:
Advantages of Tilting Rotary Furnaces
- Efficiency: The combination of rotation and tilting minimizes dead zones and ensures complete melting of the charge, maximizing yield and reducing energy consumption.
- Quality: Improved mixing and temperature control lead to high-quality molten metal, essential for producing reliable castings and alloys.
- Safety: The tilting mechanism reduces manual handling of molten metal, lowering the risk of accidents and improving operator safety.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of metals and alloys, making it a flexible solution for various metallurgical applications.
The structure and composition of tilting rotary furnace:
A tilting rotary furnace has the following structure and composition:
- Rotary Mechanism:
- Rotary Drum: A cylindrical, rotating drum where the metal charge is placed.
- Efficient Heating: Ensures even heat distribution and mixing of the molten metal.
- Tilting Mechanism:
- Tilted Pouring: Allows the furnace to be tilted to pour molten metal into molds, ladles, or casting machines.
- Precision Control: Provides careful management of the molten metal flow.
- Heating System:
- Fuel Options: Capable of using various fuels such as natural gas, diesel, propane, or electricity.
- Burners and Airflow: Includes burners and air passages for efficient combustion and heat transfer.
- Material Handling:
- Scrap Loading: Can handle different types of metal scrap, including loose pieces, compact bales, and ingots.
- Residue Handling: Rotary movement aids in managing residues like dross and slag.
- Advanced Controls:
- Temperature Control: Precise controls and monitoring systems to ensure the metal is melted to desired specifications.
- Automation: Modern furnaces often have automated control systems for enhanced efficiency and safety.
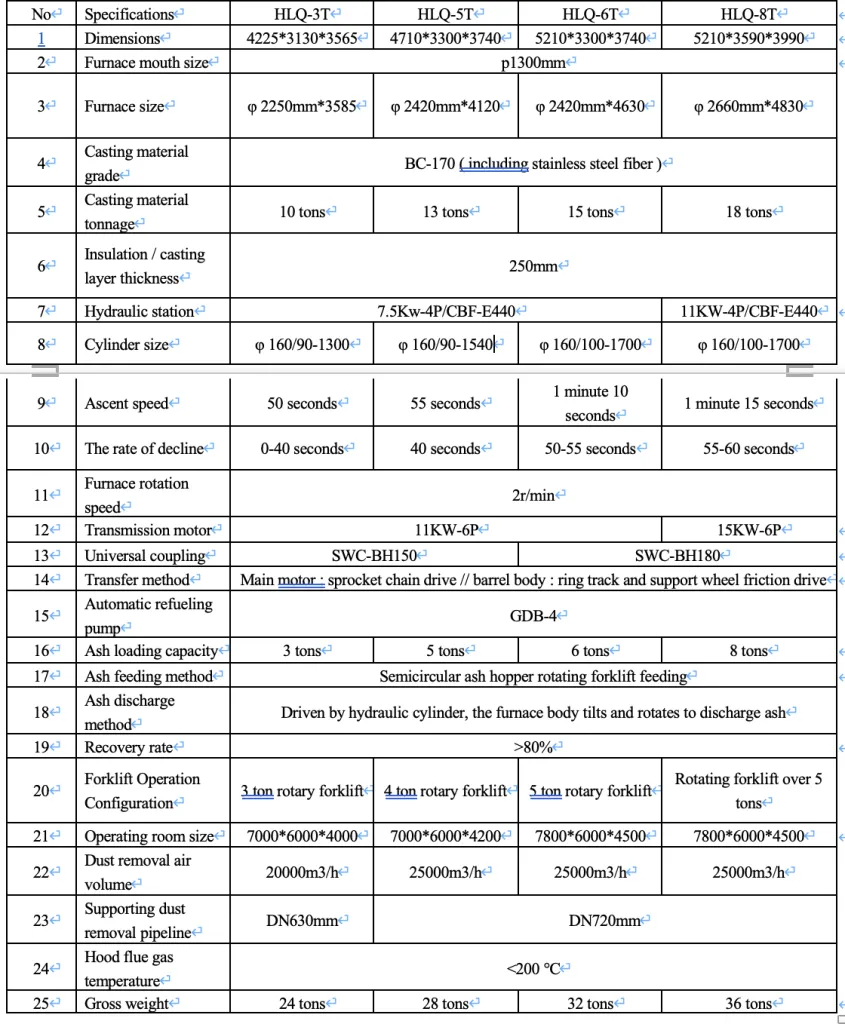
Technical Details:
 In summary, a tilting rotary furnace is a versatile and efficient industrial furnace that plays a critical role in modern metallurgy, particularly in metal recycling, foundries, and production of high-quality metal products. Its design facilitates superior metal handling, energy efficiency, and precise control, which are highly valued in metalworking industries.
In summary, a tilting rotary furnace is a versatile and efficient industrial furnace that plays a critical role in modern metallurgy, particularly in metal recycling, foundries, and production of high-quality metal products. Its design facilitates superior metal handling, energy efficiency, and precise control, which are highly valued in metalworking industries.

