Understanding the Induction Cylinder Hardening Scanner
Induction hardening is a process whereby a metal cylinder is exposed to a high-frequency alternating current, producing an intense and rapidly alternating magnetic field around it. This causes heat to be generated within the surface of the cylinder through induction, which in turn increases its hardness and resistance to wear and fatigue. An
induction cylinder hardening scanner is integral in overseeing and validating this transformation, ensuring uniformity and the attainment of the desired mechanical properties.
Introduction to Induction Hardening
What is Induction Hardening?
Induction hardening is a heat treatment process used to enhance the surface hardness of steel and other alloy components. It selectively hardens the areas that are most susceptible to wear and stress, remarkably extending the life and performance of the cylinder without affecting its toughness.
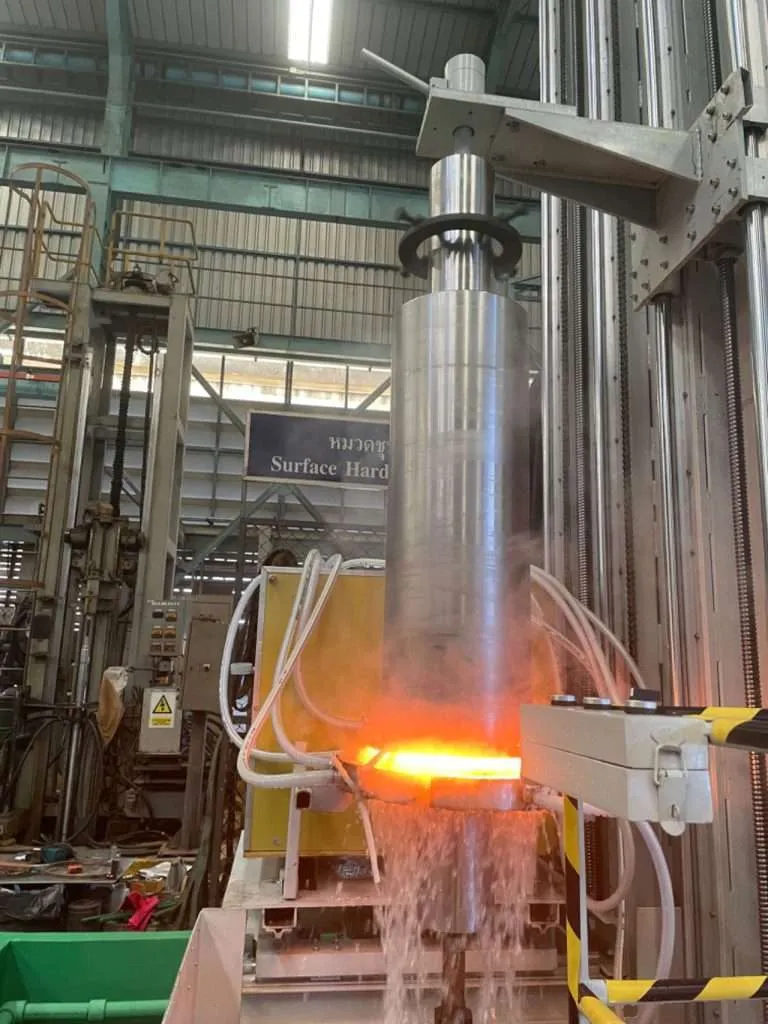 Components and Workings of an Induction Hardening Scanner
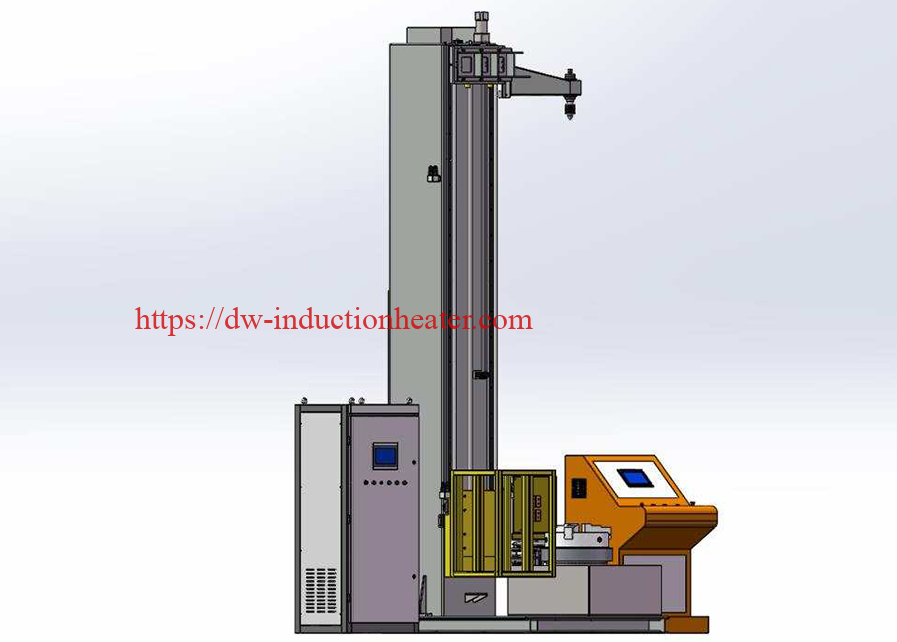
The Key Elements of the Scanner
Components and Workings of an Induction Hardening Scanner
The Key Elements of the Scanner
The
induction hardening scanner typically consists of an induction coil, a quenching system, and multiple sensors that monitor temperature, hardness, and other vital parameters in real-time to ensure the process stays within the predetermined specifications.
Analyzing Hardness Patterns with Advanced Sensors
Through the use of sophisticated sensors, the scanner reads the surface and subsurface changes as the induction hardening process is underway. The sensors report real-time data which reflects whether the desired hardness is achieved or if adjustments are necessary.
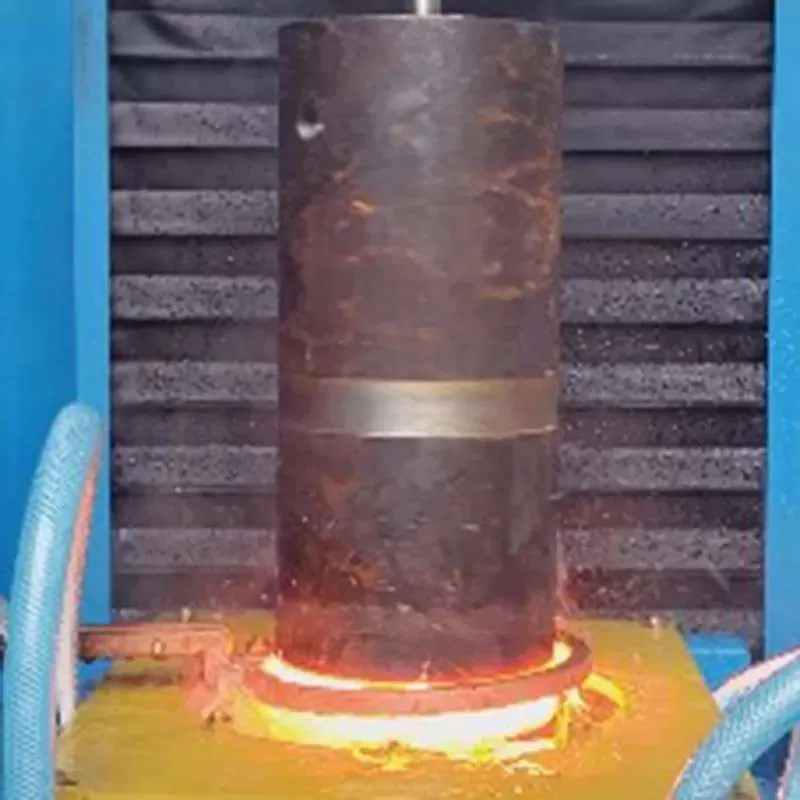

Applications and Benefits of Induction Cylinder Hardening Scanners
The Scanner’s Role in Quality Assurance
The induction cylinder hardening scanner's primary role is to guarantee that each cylinder meets stringent quality benchmarks. By providing immediate feedback on the hardening process, it ensures precision and uniformity.
Innovations Enhancing the Induction Hardening Process
Technological advancements have paved the way for induction hardening scanners to be more versatile and accurate. Innovations often include enhanced data analytics and the integration of AI to fine-tune the process through adaptive control systems.
FAQs on Induction Cylinder Hardening Scanners
Q1: How does an induction hardening scanner improve the hardening process?
A1: It enhances the process by providing real-time data and feedback, ensuring the metal reaches the exact level of hardness required with consistent quality across all parts.
Q2: Can induction hardening scanners detect overheating hazards?
A2: Yes, part of the scanner’s role is to monitor temperature levels closely throughout the process, thereby preventing overheating, which can cause warping or other defects.
Q3: Is there a significant downtime involved when installing an induction hardening scanner in a production line?
A3: While installation may require some downtime to integrate the scanner into existing systems, the long-term efficiencies and improvements in quality assurance typically outweigh this temporary pause in production.
Q4: Are these scanners compatible with all types of induction hardening machines?
A4: Most
induction hardening scanners are designed to be adaptable to various machines and setups. However, certain specifications and compatibility checks should be performed before integration.
Q5: What kind of maintenance is needed for induction hardening scanners?
A5: Regular maintenance should include software updates, sensor calibrations, and routine checks to ensure all components are functioning correctly. This helps in maintaining the accuracy and reliability of the scanner.
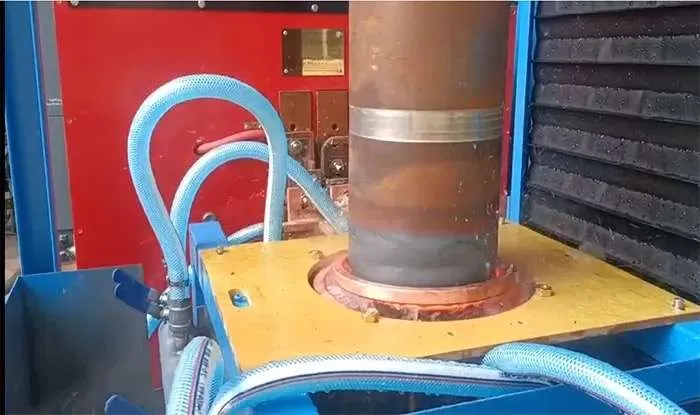

are commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing, where precise control and inspection of hardened cylindrical components are critical for product quality and reliability.


 Components and Workings of an Induction Hardening Scanner
The Key Elements of the Scanner
The induction hardening scanner typically consists of an induction coil, a quenching system, and multiple sensors that monitor temperature, hardness, and other vital parameters in real-time to ensure the process stays within the predetermined specifications.
Analyzing Hardness Patterns with Advanced Sensors
Through the use of sophisticated sensors, the scanner reads the surface and subsurface changes as the induction hardening process is underway. The sensors report real-time data which reflects whether the desired hardness is achieved or if adjustments are necessary.
Components and Workings of an Induction Hardening Scanner
The Key Elements of the Scanner
The induction hardening scanner typically consists of an induction coil, a quenching system, and multiple sensors that monitor temperature, hardness, and other vital parameters in real-time to ensure the process stays within the predetermined specifications.
Analyzing Hardness Patterns with Advanced Sensors
Through the use of sophisticated sensors, the scanner reads the surface and subsurface changes as the induction hardening process is underway. The sensors report real-time data which reflects whether the desired hardness is achieved or if adjustments are necessary.

