The
induction heating boiler works by means of an induction coil, which creates a variable magnetic field using current of 50 Hz frequency. The metal maze system, which intensifies the heat exchange, is heated by means of magnetic reversal and practically without loss transfers the released energy to the heat carrier.
The principles of induction
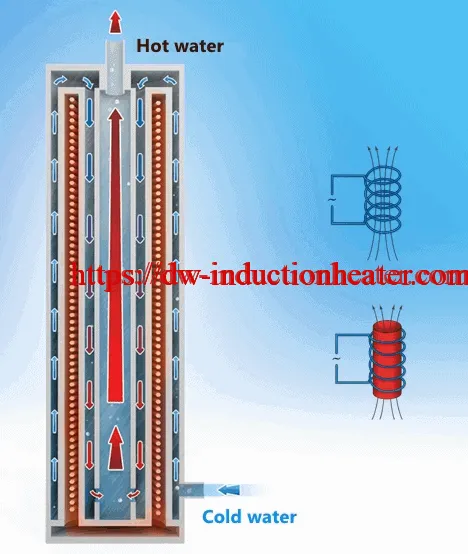
The mode of induction heating is easily illustrated using an inductor with a magnetic field, which is changed together with the current strength change. The field is closed inside the coil and the intensity depends on the current strength and the number of coil turns.
What is Induction Boiler?
An magnetic induction boiler may be the ideal solution for heating your home if the option fo gas is unavailable
where you live, or you want the benefits of having an electric-powered heating system, such as a quiet boiler and more installation flexibility.
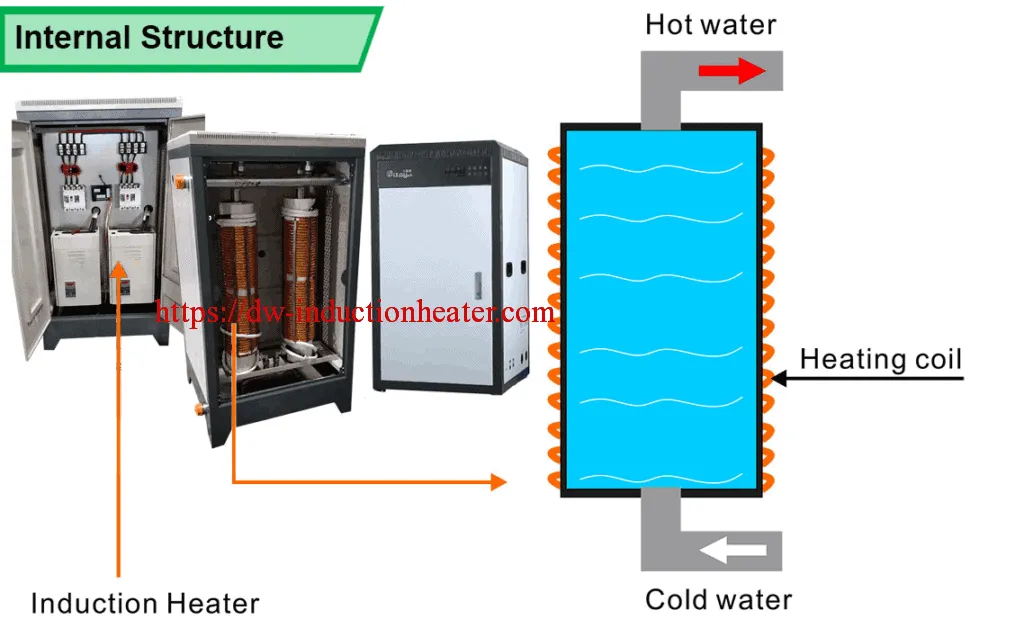
The electromagnetic induction boiler uses electricity rather than gas to heat hot water. Just like a gas boiler, it will heat up the water that warms your radiators and underfloor water pipe.

Induction heating
When placing a metal object inside the coil there will arise eddy currents, which as a result of electric resistance of metal will cause heating of the surface. Heating effect increases with the field intensity increase and depends on the material properties and the size of the coil.
In the boiler there is used an induction coil, which in addition to consumption is also a generator, as its conductor is allocated in the variable magnetic field that causes generation of reactive power. During the process of recovery, the active current, consumed from the network is very slight, and the reactive current closed in the loop is strong enough, which enables boilers SAV to use the extra power produced in the oscillating circuit and to reduce energy consumption.
The advantages of induction boilers
- • Stable high level of efficiency 99% which does not decrease during the period of operation
- • In many cases the transition to induction electric heating reduces the operating costs by an average of 30%
- • Noise and vibration free
- • Maximum scale protection
- • Complete absence of detachable connections in the construction, which eliminates the possibility of leakage
- • Operating current frequency: 50 Hz
- • Does not require highly skilled personnel for installation and maintenance
- • High power factor = 0,98 (almost all energy consumed from the network goes to the creation of heat)
- • Induction heater is characterized by a high degree of electrical and fire safety: the heating element (mazes of pipes) has no electrical connection with the inductor. The maximum temperature on the surface of the heater exceeds the temperature of the heat carrier by not more than 10-30 °C (for heaters working in heating and hot water supply systems)
- • There are no items subject to mechanical wear, no moving parts and high-loaded parts and devices
- • Service life of induction heaters is more than 30 years (when used for heating of buildings)
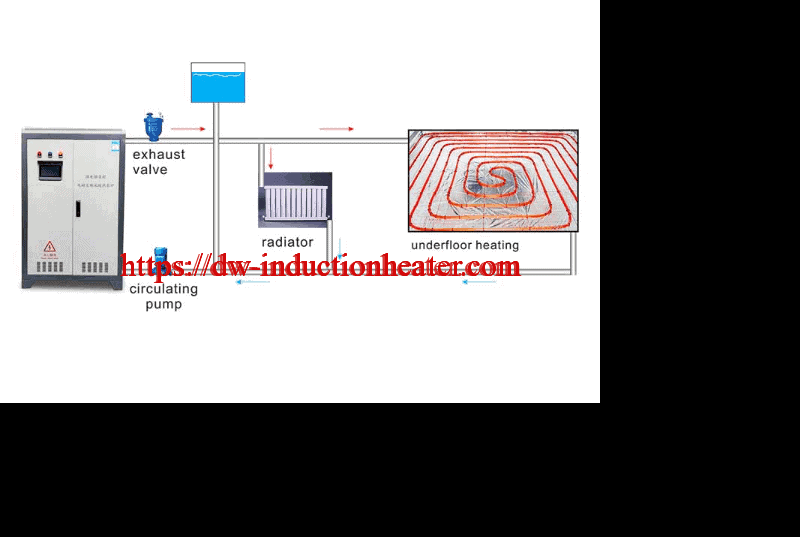
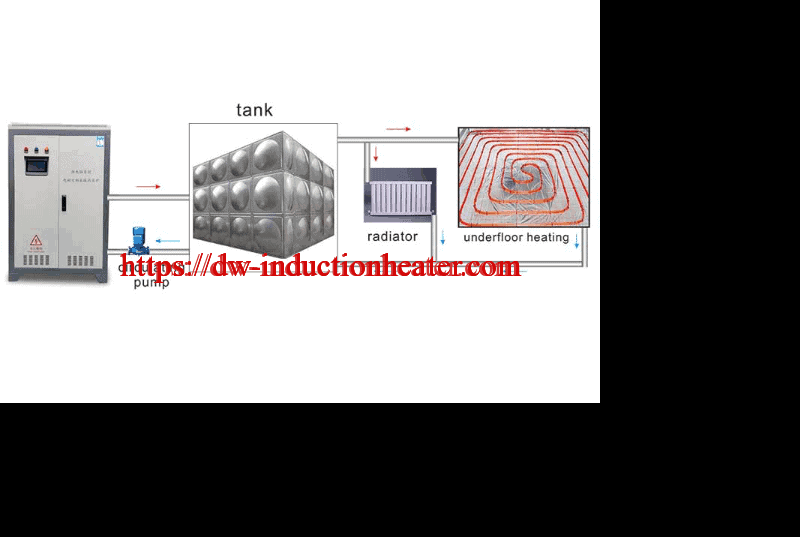
- • Compatibility with other heating systems
- • Do not require a separate installation room
- • Induction heating makes possible the use of various liquid heat carriers (water, oil, antifreeze) without prior technological preparation
- • Completely self-contained, require no preventive works during the heating season and low-season

Fields of application
The versatility of induction boilers operating at industrial current frequency makes possible to use them in various industries in an effective and profitable way
- • Standalone (decentralized) heating;
- • Combined (bivalent) heating;
- • Redundancy of heat supply sources;
- • Hot water supply;
- • Maintaining of the temperature in technologic processes, both in flow and chamber reactors;
- • Adjustment of heating processes using unstable renewable energy sources (RES) and low-grade local fuels;
- • Automated heat supply with distant (remote) control.
 The mode of induction heating is easily illustrated using an inductor with a magnetic field, which is changed together with the current strength change. The field is closed inside the coil and the intensity depends on the current strength and the number of coil turns.
The mode of induction heating is easily illustrated using an inductor with a magnetic field, which is changed together with the current strength change. The field is closed inside the coil and the intensity depends on the current strength and the number of coil turns.
 where you live, or you want the benefits of having an electric-powered heating system, such as a quiet boiler and more installation flexibility.
The electromagnetic induction boiler uses electricity rather than gas to heat hot water. Just like a gas boiler, it will heat up the water that warms your radiators and underfloor water pipe.
where you live, or you want the benefits of having an electric-powered heating system, such as a quiet boiler and more installation flexibility.
The electromagnetic induction boiler uses electricity rather than gas to heat hot water. Just like a gas boiler, it will heat up the water that warms your radiators and underfloor water pipe.



